Graphenea introduces “Easy Transfer” - the simplest method to transfer monolayer graphene onto a substrate. The company has applied its years of experience in growing and transferring superior quality graphene films to allow users to experiment with any novel substrate by utilizing Easy Transfer.
Using Easy Transfer helps users to avoid metal etching and unsafe chemical handling. Manipulation of thin film is performed at Graphenea when Easy Transfer is used. Bottom layer is removed using this process.
Graphene Film
- Growth method: CVD synthesis
- Appearance (color): Transparent
- Transparency: >97%
- Appearance (form): Film
- Number of graphene layers: 1
- Coverage: > 95%
- Thickness (theoretical): 0.345nm
- FET electron mobility on SiO2/Si: 4000cm2/Vs
- FET electron mobility on Al2O3: 2000cm2/Vs
- Grain size: Up to 10µm
- Sheet resistance on SiO2/Si: 450±40 Ohms/sq (1x1cm)
Download the Brochure for More Information
Graphene Transfer Procedure
The graphene transfer procedure can be accomplished in three simple steps, as follows:
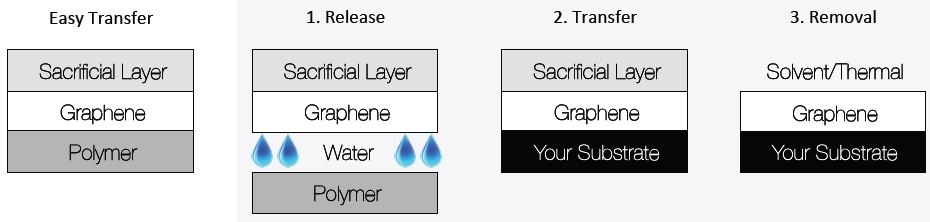
- Release: The sample has to be placed in deionized water slowly while the sacrificial layer/graphene is detached from the support film. There is no need to wet the sample initially. Once the sacrificial layer/graphene is floating, the polymer film should be removed.
- Transfer: The sacrificial layer/graphene will be floating in the water. To deposit it onto the preferred substrate, put the substrate into the deionized water and seek out the sacrificial layer/graphene from below. Graphenea recommends tilting of the substrate at 45°. The sacrificial layer/graphene/substrate must then be pulled out and allowed to dry for 30 minutes in air prior to storing it under vacuum for about 24 hours in order to prevent detachment of the graphene from the substrate.
- Sacrificial Layer Removal: There are two techniques to remove the sacrificial layer. One is using solvents. Soak the sacrificial layer/graphene/substrate in acetone for one hour, followed by a soak in iso-propyl alcohol for another one hour. Finally, blow the sample to dry it using N2. The second method is thermal treatment. The sacrificial layer/graphene/substrate should be placed inside an oven and the sample should be heated at 450°C in inert atmosphere for two hours.
Download the Brochure for More Information
Applications
- Graphene research
- Electronics
- Flexible batteries
- Conductive coatings
- MEMS and NEMS
- Aerospace industry
- Microactuators