Scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have captured the first real-time nanoscale images of lithium dendrite structures known to degrade lithium-ion batteries. The ORNL team’s electron microscopy could help researchers address long-standing issues related to battery performance and safety.
 ORNL electron microscopy captured the first real-time nanoscale images of the nucleation and growth of lithium dendrite structures known to degrade lithium-ion batteries. CREDIT: ORNL
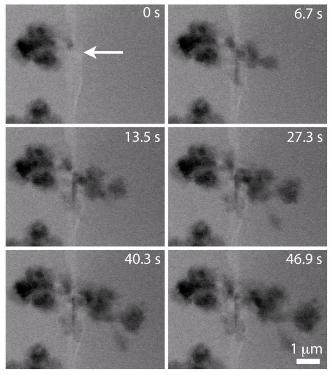
ORNL electron microscopy captured the first real-time nanoscale images of the nucleation and growth of lithium dendrite structures known to degrade lithium-ion batteries. CREDIT: ORNL
Dendrites form when metallic lithium takes root on a battery’s anode and begins growing haphazardly. If the dendrites grow too large, they can puncture the divider between the electrodes and short-circuit the cell, resulting in catastrophic battery failure.
The researchers studied dendrite formation by using a miniature electrochemical cell that mimics the liquid conditions inside a lithium-ion battery. Placing the liquid cell in a scanning transmission electron microscope and applying voltage to the cell allowed the researchers to watch as lithium deposits—which start as a nanometer-size seed—grew into dendritic structures.
“It gives us a nanoscopic view of how dendrites nucleate and grow,” said ORNL’s Raymond Unocic, in situ microscopy team leader. “We can visualize the whole process on a glassy carbon microelectrode and observe where the dendrites prefer to nucleate and also track morphological changes during growth.” Watch a video of the dendrite growth here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rpPUTM_u_PM.
In addition to imaging the structures at high-resolution, the team’s microscopy technique gathered precise measurements of the cell’s electrochemical performance. “This technique allows us to follow subtle nano-sized structural and chemical changes that occur and more importantly, correlate that to the measured performance of a battery,” said Robert Sacci, ORNL postdoctoral researcher and lead author of the Nano Letters study.
This real-time analysis in a liquid environment sets the ORNL team’s approach apart from other characterization methods.
“Usually when you run a battery over many charge-discharge cycles, you typically wait until things start failing and at that point you perform a root-cause failure analysis,” Unocic said. “Then you see there’s a dendrite—but so what? Now that we can see exactly how the dendrites are forming using our technique, we can be proactive and devise strategies for inhibiting or reducing these phenomena.”
The ORNL team believes scientists who are experimenting with different ways to tackle the dendrite problem, such as liquid additives or stronger separators, will benefit from its research.
“If you don’t understand the basic mechanism of why things happen in your devices, you’ll always be thinking, ‘Why did this happen and how do I fix it?’” Unocic said. “Until you get down to the microscopic and nanoscopic level to look at the structural and chemical evolution that’s happening in the cells—then you can’t truly address those issues that come up.”
The study is published as “Nanoscale Imaging of Fundamental Li Battery Chemistry: Solid-Electrolyte Interphase Formation and Preferential Growth of Lithium Metal Nanoclusters. Coauthors are Robert Sacci, Jennifer Black, Nina Balke, Nancy Dudney, Karren More and Raymond Unocic.
This research was supported as part of the Fluid Interface Reactions, Structures and Transport (FIRST) Center, an Energy Frontier Research Center funded by DOE’s Office of Science. The study also used resources at Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences, a DOE Office of Science User Facility at ORNL.
UT-Battelle manages ORNL for the Department of Energy’s Office of Science. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit http://science.energy.gov/.
Source: http://www.ornl.gov/