A research team from the Kansas State University has devised a novel technique that paves the way to solve a long-held issue of manufacturing graphene quantum dots at large densities with controlled size and shape.
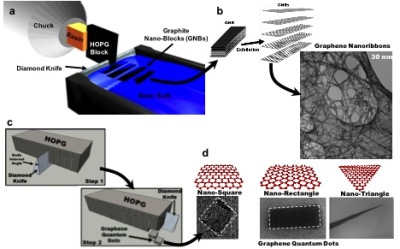 Diamond knife cuts graphite to produce graphene nanoribbons and quantum dots of controlled shape and size at high yields.
Diamond knife cuts graphite to produce graphene nanoribbons and quantum dots of controlled shape and size at high yields.
The new process, developed by Professor Vikas Berry from the Kansas State University, produces graphite nanoblocks by slicing graphite with a diamond knife. These graphite nanoblocks are precursors for producing graphene quantum dots. Exfoliation of these nanoblocks creates ultra-small carbon sheets of controlled size and shape.
The scientists are now able to manipulate the properties of graphene by controlling the shape and size for different applications, including particulate systems, composites, biomarkers, optical dyes, electronics, and solar cells. They can produce large quantities of graphene quantum dots that have a controlled structure, thus opening up the possibility to use these optically active quantum dots for optoelectronic applications such as solar cells.
It is a known fact that due to quantum confinement and edge states, graphene quantum dots’ size and shape play a key role in controlling their chemical, magnetic, optical and electrical properties. This research demonstrates an evidence of a band-gap in graphene nanoribbon films with reduced width. Moreover, with the help of simulations and high-resolution transmission electron micrographs, the researchers show that the edges of the structures obtainedare comparatively smooth and straight.
Berry informed that these graphene quantum dots show promise in a variety of applications. The research team believes that this research will lead to the field of graphene quantum dots as this novel material holds potential in various nanotechnologies. The research results have been reported in Nature Communications.
Source: http://www.k-state.edu