A research team from the Israel Institute of Technology or Technion has developed a new optical microscope capable of revealing information similar to a conventional blood test but in real-time.
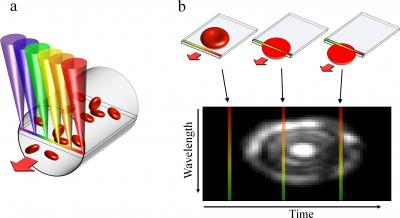 The team’s device relies on a technique called spectrally encoded confocal microscopy. (a) A single line within a blood vessel is imaged with multiple colors of light that encode lateral positions. (b) A single cell crossing the spectral line produces a two-dimensional image with one axis encoded by wavelength and the other by time. (Credit: Biomedical Optics Express)
The team’s device relies on a technique called spectrally encoded confocal microscopy. (a) A single line within a blood vessel is imaged with multiple colors of light that encode lateral positions. (b) A single cell crossing the spectral line produces a two-dimensional image with one axis encoded by wavelength and the other by time. (Credit: Biomedical Optics Express)
This optical instrument is based on spectrally encoded confocal microscopy technique, in which a light beam is split into its constituent colors, from red to violet, for producing images of blood traversing a vein. These constituent colors are arranged in a line. To analyze the blood cells in circulation, a probe is made to contact the skin of a patient and the rainbow-like light line is made to focus a blood vessel adjacent to the surface of the skin. The light gets scattered by the blood cells when they cross the line.
This scattered light is collected and studied because the scattered light’s colors carry spatial information, which is used to produce dimensional images of the blood cells by interpreting the signal over time using computer programs. This novel device having the size of a breadbox is able to capture high-resolution images of blood cells without using potentially toxic fluorescent dyes.
With the help of this optical microscope, the researchers were able to measure the average diameter of the white and red blood cells, and calculate the volume percentage of the various cell types, an essential data for most of the medical diagnoses. Besides allowing rapid blood analysis, this equipment’s portability enables it to be used in field tests for common blood disorders. This technique leverages the cells’ one-way flow to form a compact probe that is capable of imaging large count of cells, at the same time stay stationary against the skin.
The new microscope features a camera and a green LED to get a wider field of view. However, the absorption of the green light by hemoglobin restricts the device from finding a blood vessel’s depth. The researchers are now involved in the development of a second-generation instrument with higher penetration depth. They are also working on reducing the size of the device.
The researchers have reported about their novel device in Biomedical Optics Express, an open-access journal of the Optical Society.
Source: http://www.osa.org