Researchers from the San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering at the University of California engineered a method to facilitate metallic nanocrystals to self-assemble into bigger structures that could find applications in future generations of lenses and antennas.
 Self assembling nanocubes
Self assembling nanocubes
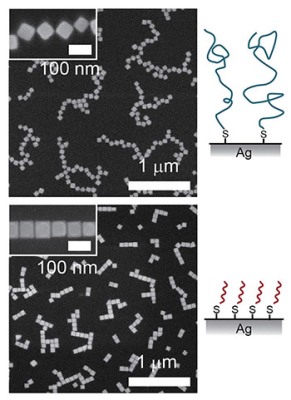
The cubic metal nanocrystals can be likened to Tetris blocks that are capable of arranging themselves into bigger structures with relative orientation. This particular field of research which is known as Nanoplasmonics involves the development of materials with structures smaller than the wavelength of light and using these materials to manipulate light.
The researchers employed nanocubes that are smaller than 0.1µ. By means of accurate orientation, the nanocubes can either focus light at various wavelengths if they are meant to serve as a lens or can confine light if they are meant to function as a nanoscale antenna. The findings could make significant contribution in the development of optical biological and chemical sensors that involve molecular interaction with light. The ability to confine light within extremely small volumes could drastically improve sensitivity of optical sensors.
The research team constructed antenna and lens structures by chemical synthesis of crystalline silver into nanocubes. They attached polymer chains to the silver nanocubes to control the interaction of the cubes for rearrangement. The team demonstrated through simulation that the attaching of short polymer chains would cause the cubes to arrange themselves normally whereas, attaching long polymer chains would lead to edge-to-edge stacking of the cubes. The two different arrangements were imaged using macroscopic films which showed that the films transmitted and reflected light of different wavelengths.
Source: http://ucsdnews.ucsd.edu