Apr 5 2016
Use of nanoparticles in many applications, e.g. for catalysis, relies on the surface area of the particles. Now scientists show how originally spherical nucleus can transform into cube with high surface-to-volume ratio. These nanocubes are available to be used in practice, and may interest many designers of new materials. The research has recently been reported in ACS Nano.
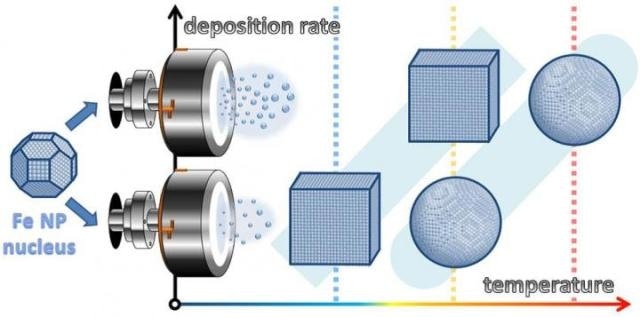 Originally close-to-spherical iron nanoparticle nuclei grow in magnetron sputter chambers either cubic or spheres. The research revealed a specific regime of temperature and deposition rates leading to thermodynamically unexpected cubic shapes of final nanoparticles. (credit: Panagiotis Grammatikopoulos)
Originally close-to-spherical iron nanoparticle nuclei grow in magnetron sputter chambers either cubic or spheres. The research revealed a specific regime of temperature and deposition rates leading to thermodynamically unexpected cubic shapes of final nanoparticles. (credit: Panagiotis Grammatikopoulos)
The efficiency of many applications deriving from natural sciences depends dramatically on a finite-size property of nanoparticles, so-called surface-to-volume ratio. The larger the surface of nanoparticles for the same volume is achieved, the more efficiently nanoparticles can interact with the surrounding substance. However, thermodynamic equilibrium forces nanostructures to minimize open surface driven by energy minimization principle. This basic principle predicts that the only shape of nanoparticles can be spherical or close-to-spherical ones.
Nature, however, does not always follow the simple principles. An intensive collaboration between University of Helsinki, Finland, and Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology, Japan, showed that in some condition iron nanoparticles can grow in cubic shape. The scientists also succeeded in disclosing the mechanisms behind this.
“Now we have a recipe how to synthesize cubic shapes with high surface-to-volume ratio which opens the door for practical applications”, says Dr. Flyura Djurabekova from the University of Helsinki.
In the researcher’s work, experiment and theory were brought together via a new mathematical model, which gives a recipe on how to select macroscopic experimental conditions to achieve the formation of nanoparticles of desired shape.
The computational work carried out in the group of Djurabekova showed the importance of kinetical processes in this surprising phenomenon, namely the competition between surface diffusion and deposition rate of atoms. The simulations showed how an originally spherical nucleus transforms into a perfect cube.
The results were recently published in the high-impact factor journal ACS Nano.
Junlei Zhao, Ekaterina Baibuz, Jerome Vernieres, Panagiotis Grammatikopoulos, Ville Jansson, Morten Nagel, Stephan Steinhauer, Mukhles Sowwan, Antti Kuronen, Kai Nordlund, and Flyura Djurabekova, Formation Mechanism of Fe Nanocubes by Magnetron Sputtering Inert Gas Condensation, ACS Nano, Article ASAP, DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.6b01024, Publication Date (Web): March 10, 2016, Copyright © 2016 American Chemical Society
Source: https://www.helsinki.fi/