Antibodies (Ab) are proteins produced by the body in response to the presence of a foreign body. Antigens (Ag) are foreign compounds that instigate the production of antibodies. They may occur free in solution or they may be bound to the surface of cells or particles such as viruses or bacteria. An antibody produced in response to a foreign body reacts with the antigen to form an immune complex (Ab-Ag) and is therefore inactivated.
Dynamic Light Scattering for Measuring Particle Size
Dynamic light scattering (photon correlation spectroscopy) is a technique that can measure the size of particles down to 1nm in diameter. Particles in suspension undergo random Brownian motion. If these particles are illuminated with a laser beam, the intensity of the scattered light fluctuates at a rate that is dependent upon the size of the particles. Analysis of these intensity fluctuations yields the velocity of the Brownian motion and hence the particle size.
Dealing with Small Particles and Dilute Concentrations
The intensity of scattered light obtained from small particles or from samples that are very dilute will be insufficient for repeatable PCS sizing measurements using a standard 10mW He-Ne laser.
One method of overcoming such problems is to use a higher efficiency detector. The Malvern Panalytical Zetasizer HS instrument contains an avalanche photodiode (APD).
This detector allows measurement of small particles and samples of low concentration without the need for a more powerful laser.
Case Study – Interactions Between Antibodies and a Virus
This application note describes dynamic light scattering measurements in which the affinity of two different antibodies for a virus sample can be studied.
Experimental Procedure
The measurements were made on a Malvern Panalytical Zetasizer 3000HS at a temperature of 25°C. The scattered light was detected at an angle of 90°.
Results
Figure 1 shows the intensity size distributions obtained from 3 repeat measurements of a sample of serum containing antibodies. The distributions were obtained from analysis of the data with the CONTIN algorithm. The distributions are monomodal with peak modes at 32nm respectively. The affinity of two different antibodies for a virus was determined by mixing each of the antibody samples with a sample of the virus and making rapid sizing measurements (every 30 seconds).
Figure 2 shows the z-average diameters (the mean diameter based on the intensity of scattered light) obtained for the mixtures of 2 antibodies with virus particles as a function of elapsed time after mixing. The increase in the z-average diameter results from the formation of the antibody-virus complex. Antibody 1 shows higher affinity for the virus indicated by the steeper slope of the curve.
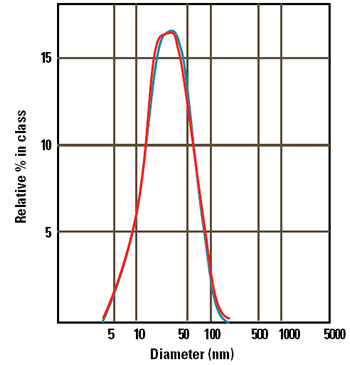
Figure 1. Intensity size distributions obtained from 3 repeat measurements of a sample of serum containing antibodies.
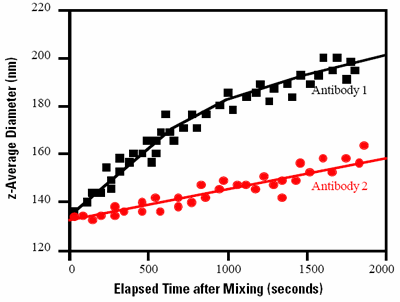
Figure 2. A plot of the z-average diameters from mixtures of 2 different antibodies with a virus as a function of the elapsed time after mixing.
Conclusions
Photon correlation spectroscopy can be used to measure the size of small particles. It is a non-invasive technique that can be used to assess the affinity of various antibodies for a particular virus.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Malvern Panalytical.
For more information please visit Malvern Panalytical.