Cell migration is one of biology’s most complex phenomenons. The word ‘invasive’ can be used to describe a motile single cell or a multicell aggregate, which penetrates through the extracellular matrix formed of neighboring tissues.
Cells that are grouped into coherent tubes, sheets or strands may undergo a type of cell migration, a process controlled by tight intercellular connections. Metastatic growth is characterized by the former, whilst wound healing is associated with the latter.
It is, therefore, important to ascertain how such seemingly similar cellular mechanisms can result in such dramatically different outcomes.
Cancer Invasion and Wound Healing: Using Cell Migration Assays
The team at Platypus Technologies has produced a large body of literature with a keen focus on measuring the rates of motility using cutting-edge assays, along with an extensive collection of work based on the basic principles of cell migration.
The team’s cell exclusion zone technology has allowed for vital mechanistic insights into cellular migration’s complex and diverse world and has helped form a greater understanding of the underlying roles played by collective migration and cell invasion in both tissue regeneration and cancer development.
When comparing the primary difference between benign and malignant cellular invasion, the most striking point to note is that invasion refers to cells that are actively attacking their surrounding tissues while migration covers normal cell functions.
At this stage, it can be helpful to understand the macro-level stages of both tissue regeneration and metastasis, respectively, in order to better grasp the differences present at the cellular level.
How do Tissues Regenerate?
There are three distinct phases of wound healing: inflammation, proliferation and maturation.
Homeostasis is the state to which our bodies naturally strive: a reasonably stable equilibrium that is maintained by various physiological processes. An inflammatory response is provoked when tissues are damaged, which is designed to maintain bodily homeostasis.
Inflammation begins when circulation platelets converge on the wound site.
These platelets congregate on the wound site to form a fibrin clot that seals the wound. Infection is mitigated by neutrophils and macrophages that also converge at the site to clear wound debris and kill invasive cellular species. Each of the mentioned cellular types migrate through the circulatory system.
More complex forms of cell migration occur in subsequent healing phases. For instance, this can be seen as epithelial cells around the damaged tissue site increase motility to cover the wound. This process is known as re-epithelialization.
A permanent structure is formed over the wound site by this new epidermis. Of course, unfortunately, complications can – and frequently do – occur in the process of wound healing.
What is the Process of Cancer Cells Metastasizing?
Though complex, a way of understanding cancer is as a group of diseases resulting from uncontrolled cell proliferation. The multiplication of cells generally occurs as part of the previously-discussed tissue regeneration process (such as in re-epithelialization).
Extreme cell proliferation occurs at enormously- increased rates, and as a result, the proliferated structures last longer than they normally should. This results in tissues accumulating in the body as masses, more commonly referred to as tumors.
Researchers have made significant strides in understanding how cancerous cells can migrate through the blood or form secondary sites by penetrating extracellular matrices (in a process known as metastasis).
This explains how two almost identical means interlink to produce dramatically different ends.
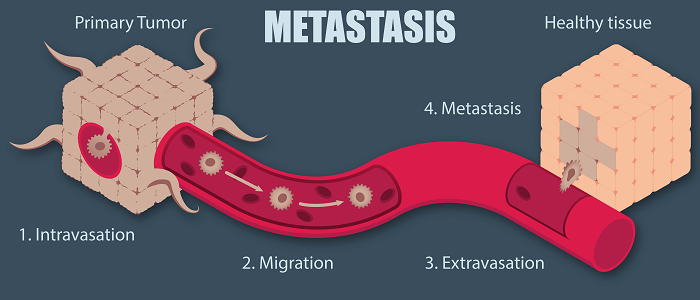
Image Credit: Platypus Technologies, LLC
Platypus Technologies: Cell Migration Assays
Platypus Technologies focuses on the power of cell exclusion zone technology, used for facilitating understanding of cell migration and invasion.
Platypus Technologies offers advanced monitoring solutions for observing the rate of directed cellular motion in real-time. Their innovative market-leading technology helps researchers gain important mechanistic insights into cell migration. To learn more, contact the Platypus Technologies team today.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Platypus Technologies, LLC.
For more information on this source, please visit Platypus Technologies, LLC.