JPK Instruments, a world-leading manufacturer of nanoanalytic instrumentation for research in life sciences and soft matter, provides a unique software package to make the display of light microscopy images together with atomic force microscopy images a seamless exercise. This package is called DirectOverlay.
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is a powerful tool to investigate a huge variety of different samples with nanometre scale resolution under physiological conditions. As well as providing topographic measurements, information about interaction forces and mechanical properties like adhesion and elasticity can also be obtained. Perfect integration of AFM with an optical setup can increase the range of applications and opens up many possibilities for correlating structural information with optical information such as functionalized labelling of certain components.
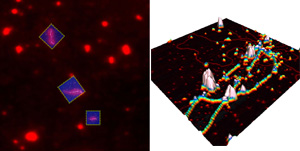 An example of the power of DirectOverlay from JPK: A fluorescence image highlights three individual labelled DNA molecules while the 3D image zooms in to a high resolution 700nm AFM image. (Sample courtesy of Dr. M. Modesti, CNRS Marseilles)
An example of the power of DirectOverlay from JPK: A fluorescence image highlights three individual labelled DNA molecules while the 3D image zooms in to a high resolution 700nm AFM image. (Sample courtesy of Dr. M. Modesti, CNRS Marseilles)
To achieve the perfect combination of optics and AFM at the molecular scale, distortions must be prevented. This will result in two images, such as optical and AFM images, that do not perfectly overlay. Reasons for distortions include aberrations arising from the lenses and mirrors of the optics system. This nonlinear stretching, rotating and offsetting of optical images are present in nearly all types of optical setups.
To generate a seamless overlay of both techniques, JPK developed a cutting-edge calibration method, called DirectOverlay, which uses the accuracy of the AFM closed-loop scanning system to enable a true display of absolute angles and length coordinates. The calibration procedure is done automatically and uses the known positions and offsets of the cantilever to calibrate the optical image into the AFM coordinates. To generate a perfect match of the optical and AFM image, 25 or more points are used in the calibration algorithm. At each point, an optical image is acquired and the position of the cantilever tip is automatically detected in each optical image without needing input on cantilever angle, shape or magnification. The algorithm then performs a nonlinear conversion and, as a result, the optical image is corrected for any lens imperfections and converted into the linearized AFM length coordinates. This provides a perfect integration of optical and AFM data with sub-diffraction limit precision.
Finally, the calibrated optical image is transferred into the JPK SPM software, so that AFM scan regions can be selected within the optical image. Direct "in optical image" selection of AFM measurements (imaging, mapping and force spectroscopy) leads to more efficient experiments and reduces dramatically overview image scanning in AFM.