Prof. Markus Pollnau and co-workers at the MESA+ Institute for Nanotechnology at the University of Twente have developed a rare-earth-ion-doped optical amplifier with performance comparable to semiconductor amplifiers.
Signal amplification
Amplification of optical signals is critical in photonics applications. Semiconductor optical waveguide amplifiers have high gain per unit length (~1000 dB/cm), but suffer from spatial and temporal gain pattering effects.
In comparison, fiber amplifiers doped with trivalent rare-earth ions like Er3+ combine good overall gain with low noise and negligible non-linearities. However, this comes at the cost of having to use several meters of fiber length, making them unsuitable for on-chip applications.
By engineering the host material, dopant concentration, and geometry the MESA+ scientists were able to increase the modal gain per unit length of rare-earth-ion-doped waveguide amplifiers to ~1000 dB/cm.
As good as semiconductor amplifiers
"Our highest measured gain of 935 dB/cm is two orders of magnitude higher than previously demonstrated in any rare-earth-ion-doped amplifier and similar to the best results reported for semiconductor amplifiers," says Dimitri Geskus, lead author on the paper.
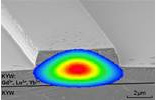
The approach uses the family of monoclinic potassium double tungstates KY(WO4)2, KGd(WO4)2, and KLu(WO4)2. Yb3+ ions doped into these materials possess some of the highest transition cross-sections observed in dielectric materials.
Besides their applicability as on-chip amplifiers for high-bit-rate data transmission at signal wavelengths around 1 ìm, these new rare-earth-ion-doped amplifiers may be used to provide optical gain in nanophotonic devices, such as nanoamplifiers and nanolasers, and may enable lossless propagation in plasmonic nanostructures.
The research is reported in the first issue of Advanced Optical Materials, a new section in Advanced Materials (2010 IF: 10.880) from Wiley-VCH dedicated to exploring light-matter interactions.