Apr 30 2013
Anasys Instruments reports on the recent publication from the University of Illinois which describes the development of a novel technique for chemical identification at the nanometer scale based on AFM-IR. The work is described in a paper published in the Review of Scientific Instruments 84.
For more than 20 years, researchers have been using atomic force microscopy (AFM) to measure and characterize materials at the nanometer scale. However AFM-based measurements of chemistry and chemical properties of materials were generally not possible, until now.
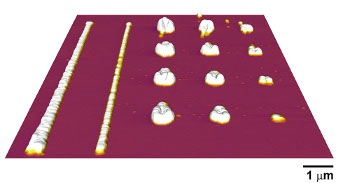 The chemical properties of these polymer nanostructures were measured using AFM-IR from Anasys Instruments.
The chemical properties of these polymer nanostructures were measured using AFM-IR from Anasys Instruments.
Researchers at the University Illinois report that they have measured the chemical properties of polymer nanostructures as small as 15 nm, using a novel technique called atomic force microscope infrared spectroscopy (AFM-IR*). The article, "Atomic force microscope infrared spectroscopy on 15nm scale polymer nanostructures," appears in the Review of Scientific Instruments 84, published by the American Institute of Physics.
"AFM-IR is a new technique for measuring infrared absorption at the nanometer scale," explained William P. King, an Abel Bliss Professor in the Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering at Illinois. "The first AFM-based measurements could measure the size and shape of nanometer-scale structures. Over the years, researchers improved AFM to measure mechanical properties and electrical properties on the nanometer scale.
"These infrared absorption properties provide information about chemical bonding in a material sample, and these infrared absorption properties can be used to identify the material," added King, who is also the director of the National Science Foundation (NSF) Center for Nanoscale Chemical-Electrical-Mechanical Manufacturing Systems at Illinois. "The polymer nanostructures are about an order of magnitude smaller than those measured previously."
The research is enabled by a new way to analyze the way the nanometer-scale dynamics within the AFM-IR system. The researchers analyzed the AFM-IR dynamics using a wavelet transform, which organizes the AFM-IR signals that vary in both time and in frequency. By separating the time and frequency components, the researchers were able to improve the signal to noise within AFM-IR and to thereby measure significantly smaller samples than previously possible.
The ability to measure the chemical composition of polymer nanostructures is important for a variety of applications, including semiconductors, composite materials, and medical diagnostics. The authors on the research are Jonathan Felts, Hanna Cho, Min-Feng Yu, Lawrence Bergman, Alex Vakakis, and William P. King. The article is available online.
*AFM-IR is a product from Anasys Instruments, Inc. For more information on AFM-IR and its applications, please visit the Anasys web site: www.anasysinstruments.com.