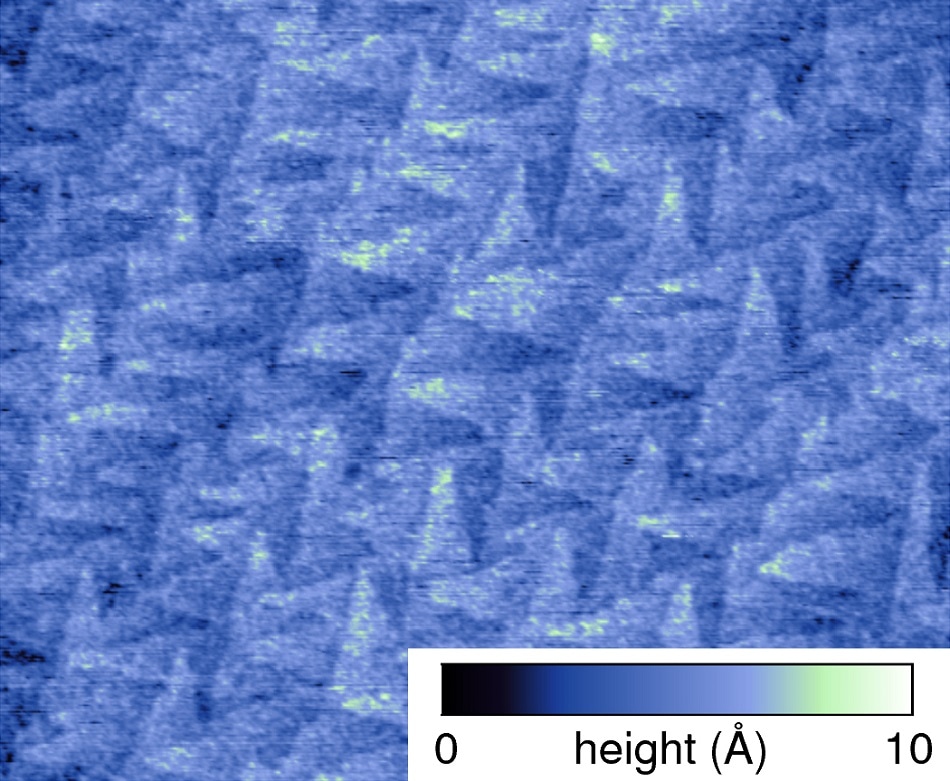
Ultra-low roughness epitaxial silicon wafer imaged on the Asylum Research Jupiter XR large-sample AFM. The roughness (Sa) for this 1 µm scan area was measured at only 0.902 Å.
New substrate preparations, thin film deposition technologies, and coating processes are producing ultra-low roughness surfaces that are below the measurement resolution of conventional optical and stylus profilometry tools. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) has long been recognized as useful for characterizing roughness on the nanometer and even sub-nanometer scales. Next-generation AFMs like the Asylum Research Jupiter XR large-sample AFM are now making these measurements simpler, faster, and more reproducible.
The new white paper by Asylum Research compares the Jupiter XR AFM to other surface roughness measurement tools and highlights its advantages. A series of examples drawn from the semiconductor, data storage, glass, and paper industries demonstrate the speed, precision, and reproducibility of the Jupiter XR. Readers will learn where AFM is the preferred tool for these measurements and why upgrading their current AFM capabilities could help drive process improvements and productivity.
The Jupiter XR AFM features a fully-addressable 200 mm sample chuck, simple and intuitive software control of system setup including laser and detector alignment, automated optimization of imaging parameters, automated multi-site imaging and analysis, and Asylum Research’s unique blueDrive tapping mode for improved tip lifetime and measurement repeatability. It is also the world’s most versatile large-sample AFM, incorporating Asylum Research’s extraordinary range of capabilities and accessories and a modular design that supports future expansion. The Jupiter XR is the ideal research platform for research environments, high-throughput industrial applications and failure analysis labs. No matter the application, no other large-stage AFM can match Jupiter’s ease of use, speed, performance and flexibility.
For more information see https://afm.oxinst.com/roughness.