|
Nanostructured metal and alloy powders may be produced either via the reduction or co-reduction of metal salts using alkaline-triorganohydroborates or using the “polyol”- or the “alcohol-reduction” pathways.
Triorganohydroborate Reduction
The triorganohydroborate reduction of e.g. Pt-salts yields Pt nanopowders of ca. 3 – 4nm size with purities of > 95% . The size distribution, however, is relatively broad and the product is contaminated with small residues of alkaline halides.
Polyol Method
Via the Polyol Method (see equation below) relatively large Pt nanopowders (e.g. 5 – 13nm) are obtained in > 99% purity. The reduction is based on the decomposition of the ethylene glycol and its conversion to diacetyl. N.
Alcohol Reduction Method
Toshima from the Science University of Tokyo in Yamaguchi has introduced the alcohol reduction method in the field of nanopowder synthesis. Alcohols such as methanol, ethanol or propanol work simultaneously as solvents and as reducing agents, being oxidized to aldehydes or ketones. Refluxing metal salts or complexes (such as H2PtCl6, HAuCl4, PdCl2, RhCl3 in an alcohol/water solution (1/1, v/v) yields nanocrystalline metal powders in the absence of stabilizers.
In the case of Pt, the alcohol reduction of H2PtCl6 gives Pt(0) particles of ≈ 3nm size, however with a broad size distribution, and moderate purity (80 – 90%). It should be mentioned here that in the presence of protective polymers such as polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), homogeneous colloidal dispersions, e.g. nanometal Pt colloids of 2.7nm size are obtained.
Applications of Metal Nanopowders
Metal nanopowders are of considerable interest in industrial powder technology, metallurgy, and in catalysis.
Metal Nanoparticles
In contrast to Metal Nanopowders which tend to agglomerate to larger grains and where Electron Microscopy shows large particle sizes with a relatively broad size distribution, “Metal Nanoparticles” generally exhibit small sizes, well defined and regular shapes and have histograms with a narrow size distribution curve (i.e. a good “monodispersity”). In case of Platinum, spherical nanoparticles of 4nm ± 0.5nm size are available from pre-prepared 4nm Pt-NR4Cl Organosols (see below) by removing the colloidal stabilizer (i.e. the NR4Cl) from the particle surface via repeated washing.
Thermolysis of Co2(CO)8
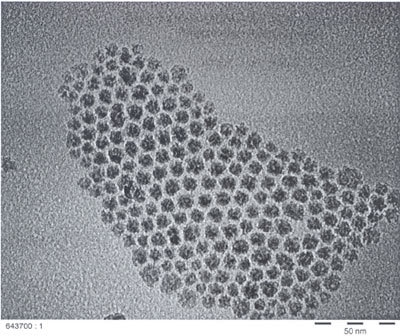
Recently, a novel, size-selective preparation route was found for the manufacture of air stable “monodispersed” colloidal cobalt nanoparticles via the thermolysis of Co2(CO)8 in the presence of aluminum alkyls. X-ray absorption near edge structure measurements have proven that subsequent “smooth air-oxidation” provides long term air-stable zerovalent magnetic cobalt particles of c.a. 10nm ± 0.5nm size (see Fig. 1). A similar procedure leads to zerovalent, air-stable nanoparticles of Ni, Fe, and to Fe/Co alloys.
|
|
|
Figure 1. TEM micrograph of air-stable 10 nm cobalt particles.
|
Applications of Metal Nanoparticles
Some interesting applications of these materials may soon develop in metallurgy and special fields of powder technology. In wet form these monodisperse Fe-, Co-, Ni- and Fe/Co alloy particles may be transformed into powerful magnetic fluids (see below).
A complete list of references can be found by referring to the original document.
|