Dec 17 2018
Nanotechnology has turned out to be an intriguing strategy toward solving challenges in the field of medicine in the latest studies. Dr Jose Manuel Cornejo Bravo has shown the use of electrospun polymeric nanofibers as an appealing method for drug delivery systems application.
 Drugs loaded and biopolymers used as matrices. (Image credit: José Manuel Cornejo Bravo et al., Bentham Science Publishers)
Drugs loaded and biopolymers used as matrices. (Image credit: José Manuel Cornejo Bravo et al., Bentham Science Publishers)
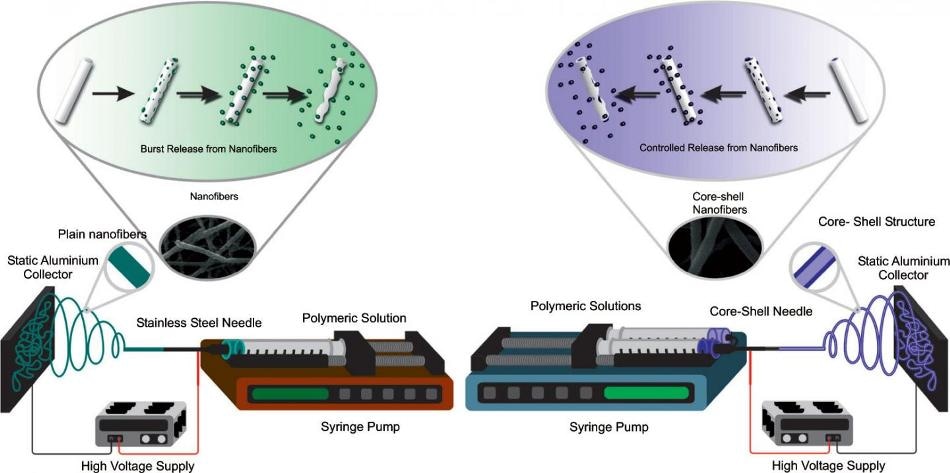
Electrospun polymeric nanofibers have a high surface-to-volume ratio, thereby considerably improving certain processes like drug loading, cell binding and proliferation, and mass transfer processes. Optimization of drug delivery is possibly the most significant application of electrospinning; it can be realized by using these materials for the regulated release of active substances such as anticancer agents, antibiotics, and macromolecules such as DNA and proteins.
This technique enhances the treatment process since it is possible to load drugs with low solubility into fibers, thus enhancing their bioavailability while also achieving controlled release. Dr Bravo’s study offers an outline of reported drugs loaded into fibers, which can be used as drug delivery systems. Drugs that have different biological functions—for example, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, anti-histamine, anti-microbial, palliative, cardiovascular, contraception, and gastrointestinal—were used for this purpose.
Together with the drugs used, the electrospinning method adopted for each system and also the polymers used as matrices for nanofiber formulation were also pertinent to the study. Different combinations of electrospinning methods and polymers best suited for the drug delivery system were used for testing the drug. When used in such synergy on the whole, electrospun polymeric nanofibers turned to be considerably more beneficial over other drug delivery systems. According to Dr Bravo, enhancement to these techniques might require further studies on the fabrication, characterization, and design of relevant nanomaterials.
Source: https://benthamscience.com/