| In the USA, which spent approximately 600 million $ public funds on nanotechnology in the year 2002 in the framework of the National Nanotechnology Initiative (NNI), nanotechnology has substantially higher importance for space technology than in Europe. This, for example, is manifested through the fact that NASA had its own nanotechnology budget of 46 million $ in 2002. The nanotechnology research of NASA can be assigned to four main directions: • Materials (11 million $, controlled by NASA Langley Laboratory), • Electronics and data processing (15 million $, controlled by NASA • Ames Laboratory), • Sensors and Components (10 million $, controlled by NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory), • Basic research. | 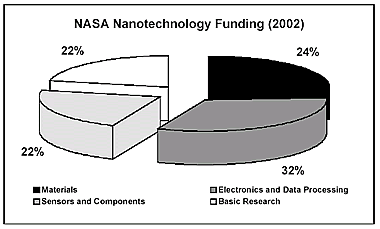
| | Figure 1. Planned distribution of 46 million $ nanotechnology funds of the NASA in the year 2002. | How NASA is Planning to Use Nanotechnology in its Space Projects Many of the nanotechnology objectives of NASA aim at a long-term time horizon, and are more or less visionary at present. One main goal is a significant increase in spacecraft capabilities with simultaneous mass reduction and miniaturization, which can not be achieved with conventional technologies. A new era of robotic exploration of the solar system is to be proposed by application of nanotechnology, among other technologies, through the development of small economical spacecrafts with high autonomy and improved capabilities. Furthermore, nanotechnological diagnostics and therapy procedures will improve life support systems, and an autonomous medical supply for astronauts which will pave the way for long-term and more complex manned space missions. Nanotechnological roadmaps of NASA reach up to 20 years into the future (see figure 2). | 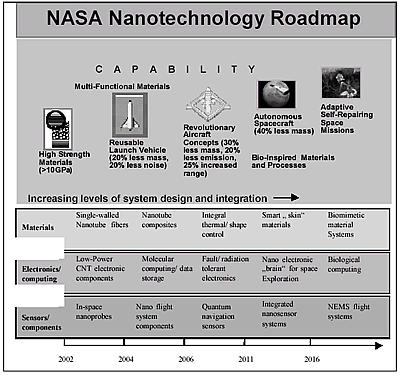
| | Figure 2. NASA Nanotechnology Roadmap. | NASA’s Research Mainly Focuses on the ‘Bottom Up’ Techniques of Molecular Nanotechnology The long-term nanotechnology research approaches of NASA, most of which are at present still in the range of basic research, are based predominantly on ‘Bottom up’ strategies of the molecular nanotechnology. That is to be understood as the controlled building of materials and structures from molecular components, by linkage of physical, chemical and biological principles. The control and technical utilization of molecular biological functions and self-assembly phenomena play an important role here. The vision of intelligent, adaptive and evolvable space systems as proposed by NASA scientists are based on the convergence of nanotechnological, biotechnological and information technological research fields (see figure 3). | 
| | Figure 3. Visionary technological developments by convergence of nanotechnology, biotechnology and information technology. | The Main Nanotechnology Sectors that NASA is Exploring Main areas of NASA nanotechnology research are (see table 1): • Nanomaterials (high strength materials, materials with programmable, intrinsic sensing and compensating properties, etc); • Nanoelectronics (data processing and communication systems with minimized energy consumption, highly integrated nanodevices for miniaturized space systems, etc); • Biomolecular nanotechnology (Lab-on-a-chip systems for biomedical and scientific in-situ detection, nanotechnological methods for diagnostics, therapy and autonomous self-medication of astronauts, etc). Critical Nanotechnology Products for NASA Nano-Engineered Materials • High strength/mass, smart materials for aerospace vehicles and large space structures, • Materials with programmable optical/thermal/mechanical/other properties, • Materials for high-efficiency energy conversion and for low temperature coolers, • Materials with embedded sensing/compensating systems for reliability and safety. Nanoelectronics • Devices for ultra high capability, low-power computing & communication systems, • Low-power, integratable nanodevices for miniature space systems, • Bio-inspired adaptable, self-healing systems for extended missions, • Quantum devices and systems for ultra-sensitive detection, analysis and communication. Biomolecular Nanotechnology • Bio-geo-chem lab on a chip for in-situ science and life detection, • Nanoscale sensing, assessment and therapeutics delivery for medical autonomy, • Molecule-to-organism bio process modelling, digital human and cybermedicine, • Tools for direct study of space-induced medical effects and counter-measures. Carbon Nanotubes are Important to NASA’s Research and Have Many Potential Industry Applications An important element of the nanotechnology research of NASA is the use of materials and components, which are based on carbon nanotubes. For this, a multiplicity of potential applications is postulated within the range of structure materials, nanoelectronics, sensor technology and biomedicine. NASA will co-operate in some areas with other organizations: • Materials (Department of Defense), • Radiation-hard devices and materials (Department of Defense), • Biosensors, lab-on-a-chip-Systems, environmental monitoring (Department of Energy, Department of Defense, NIH), • Drug delivery, non-invasive health monitoring (National Institutes of Health), • Miniaturized space systems (Department of Defense), • Efficient energy generation and storage (Department of Energy). NASA’s Partnership Work with Industry and the Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) Project Also, in co-operation with enterprises, NASA forwards developments within the range of nanotechnology. Here, in particular, the Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) programme of NASA should be mentioned, which promotes technology developments through small enterprises. This concerns predominantly application-orientated research for a short to medium-term time horizon. This research deals, in particular, with applications of nanomaterials and nanolayers. Also, in the frame of SBIR programmes of other US agencies, in particular the DoD, nanotechnological developments are promoted with relevance for the space sector. |