Mar 4 2009
Theoretical physicists from Argonne National Laboratory, US, and RIKEN's Advanced Science Institute, Wako, have constructed a general theory for describing the characteristics of an unusual and newly discovered system of particles, a chain of "spin-1/2 bosons".
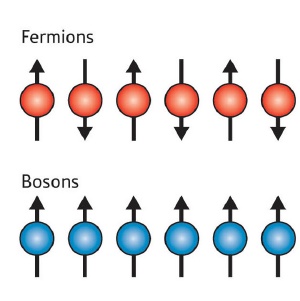 The spins on a chain of fermions (top) point in alternating directions, whereas the spins on a chain of bosons (bottom) all point in the same direction. In the latter case, this leads to the emergence of acoustic and spin wave excitations with markedly different spectra. According to the new theory, such differences should be evident in the way a 1-D system of ultracold bosonic atoms absorbs different frequencies of light.
The spins on a chain of fermions (top) point in alternating directions, whereas the spins on a chain of bosons (bottom) all point in the same direction. In the latter case, this leads to the emergence of acoustic and spin wave excitations with markedly different spectra. According to the new theory, such differences should be evident in the way a 1-D system of ultracold bosonic atoms absorbs different frequencies of light.
Most particles in the Universe are either fermions or bosons. Fermions and bosons may be distinguished by a quantum mechanical property known as spin, which determines a particle’s magnetic moment. Fermions, which include electrons and protons, have a spin of 1/2. And bosons, which include photons of light and certain atoms and molecules, always have a spin of 0 or multiples of 1. However, scientists recently discovered that bosons in the form of atoms that have been cooled to a temperature of near absolute zero can behave as if they had a spin of 1/2.
“When certain ultracold bosonic atoms are held in one-dimensional trap, each can be in one of two internal states. These two states can be regarded as up and down components of an effective spin-1/2 particle. Technically, these are referred to as isospin-1/2 bosons, but theoretically there is little difference between spin and isospin,” explains RIKEN's Akira Furusaki who, along with Konstantin Matveev from Argonne, built the theory to describe how such particles interact*.
Systems of one-dimensional fermions have been studied for decades because they can be realized experimentally in solid-state systems such as quantum wires and carbon nanotubes. Consequently, their behavior is now well established and described by the so-called Tomonaga–Luttinger theory. Matveev and Furusaki’s theory now provides a framework for describing the behavior of a chain of spin-1/2 bosons.
Matveev and Furusaki’s theory begins by recognizing that the spins of a chain of bosons prefer to point in the same direction, whereas chains of fermions arrange themselves so that their spins point in alternating directions. This means that a chain of spin-1/2 bosons can support both acoustic waves?formed by localized fluctuations in the density of particles along a chain?and spin waves?formed by deviations in the orientation of spins along a chain.
The spectra of acoustic waves and spin waves are markedly different, which affects the way in which a chain of ultracold spin-1/2 boson atoms absorbs different frequencies of light. The authors say this provides a relatively straightforward means to test their theory, and gain new insight into the behavior of these and other bosonic systems.
*Matveev, K. A. & Furusaki, A. Spectral functions of strongly interacting isospin-1/2 bosons in one dimension. Physical Review Letters 101, 170403 (2008).