In an article published in the journal ACS Omega, it was shown that nanoparticles introduced to nanofluid fuels changed the fuel's conductive and physical properties, enhancing it for use in aerospace applications.

Study: Effect of Nanoparticle Concentration on Physical and Heat-Transfer Properties and Evaporation Characteristics of Graphite/n-Decane Nanofluid Fuels. Image Credit: aapsky/Shutterstock.com
Nanofluid Fuels: A Future to Behold
A nanofluid is a fluid that contains nanoparticles, which are nanometer-sized particles. These solutions are colloidal nanoparticle suspensions in the base liquid that have been synthesized.
Carbides, oxides, metals, and carbon nanotubes are commonly employed as nanoparticles in nanofluids.
Nanofluid is made by floating a tiny number of nanoparticles in a base fluid such as water, glycol, or other similar liquids, with or without stabilizing procedures.
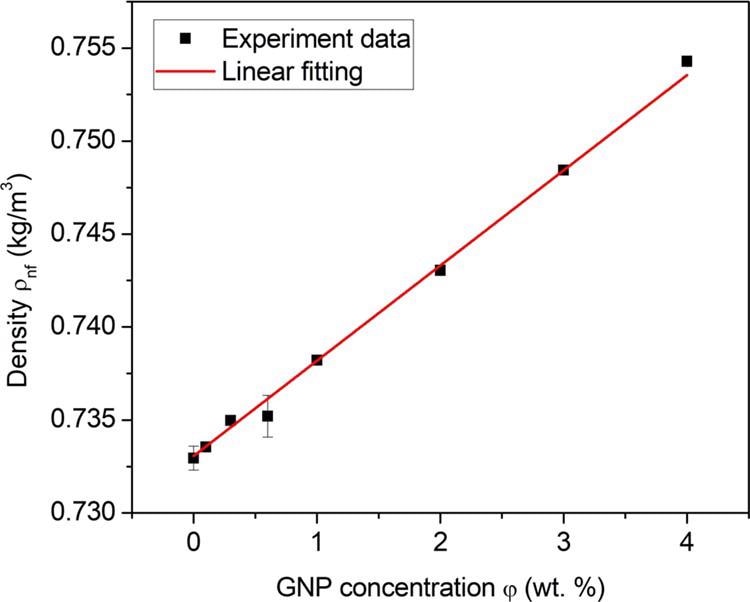
Figure 1. Density of GNP/n-decane nanofluid fuels under different GNP concentrations (SP-80 of 0.5 vol %, 25 °C). Li, S., Yang, Q., et al. (2022).
Nanofluid fuels with energetic nanoparticles (NPs) are indeed a prospective high-density fuel because NPs may dramatically increase the density and energy of the fuel.
The surface change prevents NPs from clustering together and causing them to float in the fuel.
Nanofluids, when used as fuels, offer certain advantages over their microfluid counterparts such as high flashpoints and effective heat conductive properties.
A Look into More Traditional Fuel Choice and the Problems
Traditionally, n-decane has been proposed as a possible replacement fuel for aerospace kerosene in turbine and ramjet engines.
As n-decane has strong thermal stability and low saturated vapor pressure, it can fulfill huge energy consumption demands while also lowering CO2 emissions.
Previous research has demonstrated that single n-decane species and binary mixtures of these species might be utilized as alternative fuels.
Other research showed that binary mixes of n-decane with other fuels, such as n-decane plus toluene, might be proposed as diesel, gasoline, and kerosene surrogates.
Proposed Solutions – Nanoparticles
One way for increasing the efficiency of n-decane use is to add nanoparticles (NPs) to the n-decane to produce suspensions, resulting in n-decane-based nanofluid fuels.
Nanofluid fuels, which suspend NPs (1 to 100 nm) inside a base fuel, are a relatively new type of fuel.
They have shown their potential to produce energy and management solutions for commercial processes such as vehicles (Internal Combustion engines), avionics, nuclear power, and electricity production.
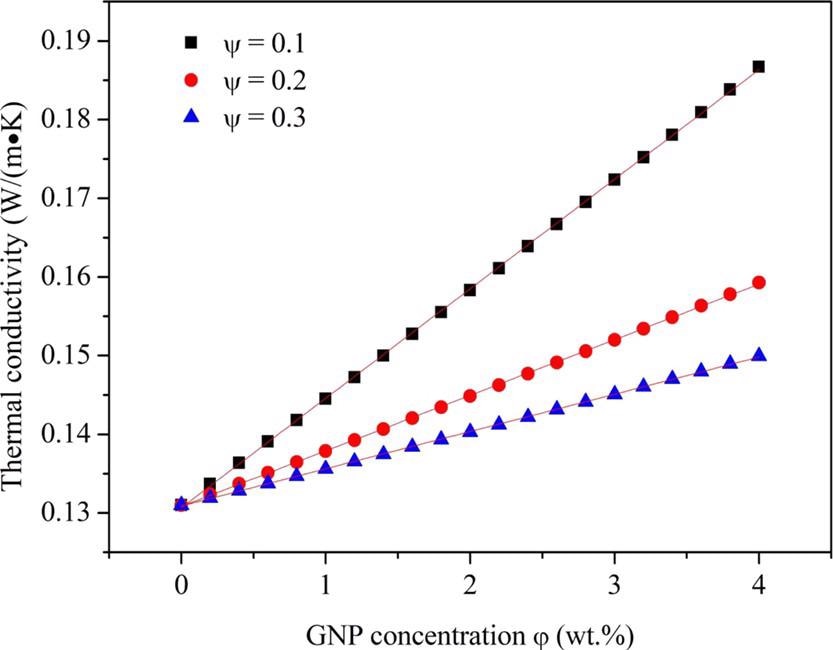
Figure 2. Thermal conductivity of GNP/n-decane nanofluid fuels under different GNP concentrations (without the surfactant of SP-80). Li, S., Yang, Q., et al. (2022).
These types of NPs can be further classified into 3 different types; metallic, metal-oxide and carbon-based, out of which, the first two lead to blockage in the combustion chamber and leave toxic residue, rendering the engines useless after repetitive use.
On the other hand, carbon-based NPs are environment friendly as they leave behind only water and carbon dioxide after combustion, which is non-toxic for biological life.
This motivated the researchers to study graphite/n-decane binary fuel composition, here referred to as Graphite Nanoplatelets (GNP), in this investigation.
Key Findings in this Paper
The authors wanted to answer two questions in this investigation.
Firstly, how the GNP concentration affects the physical parameters such as density, thermal conductivity and latent heat of vaporization and then to compare it to the obtained solution with the traditional n-decane.
Secondly, what are the optimum concentrations of GNPs affecting the physical properties?
The amount of GNPs added has a significant impact on the heat transfer and physical characteristic, as well as the rate of temperature increase and vaporization. Furthermore, as the vaporization of the base fluid progresses, the GNP concentration steadily rises, potentially deviating from the traditional d2-Law.
As GNP concentration rises, researchers discovered a linear increase in density and heat transfer, a binomial increase in viscosity, and a binomial impact on surface tension. However, the boiling point nearly stays constant as well as the latent heat of vaporization mostly decay.
For evaporation performance, a threshold GNP content of 1.75 wt % occurs.
The rise in GNP concentration favors evaporation. The evaporation performance degrades when GNP concentration is increased from 1.75 wt % to 4.0 wt %.
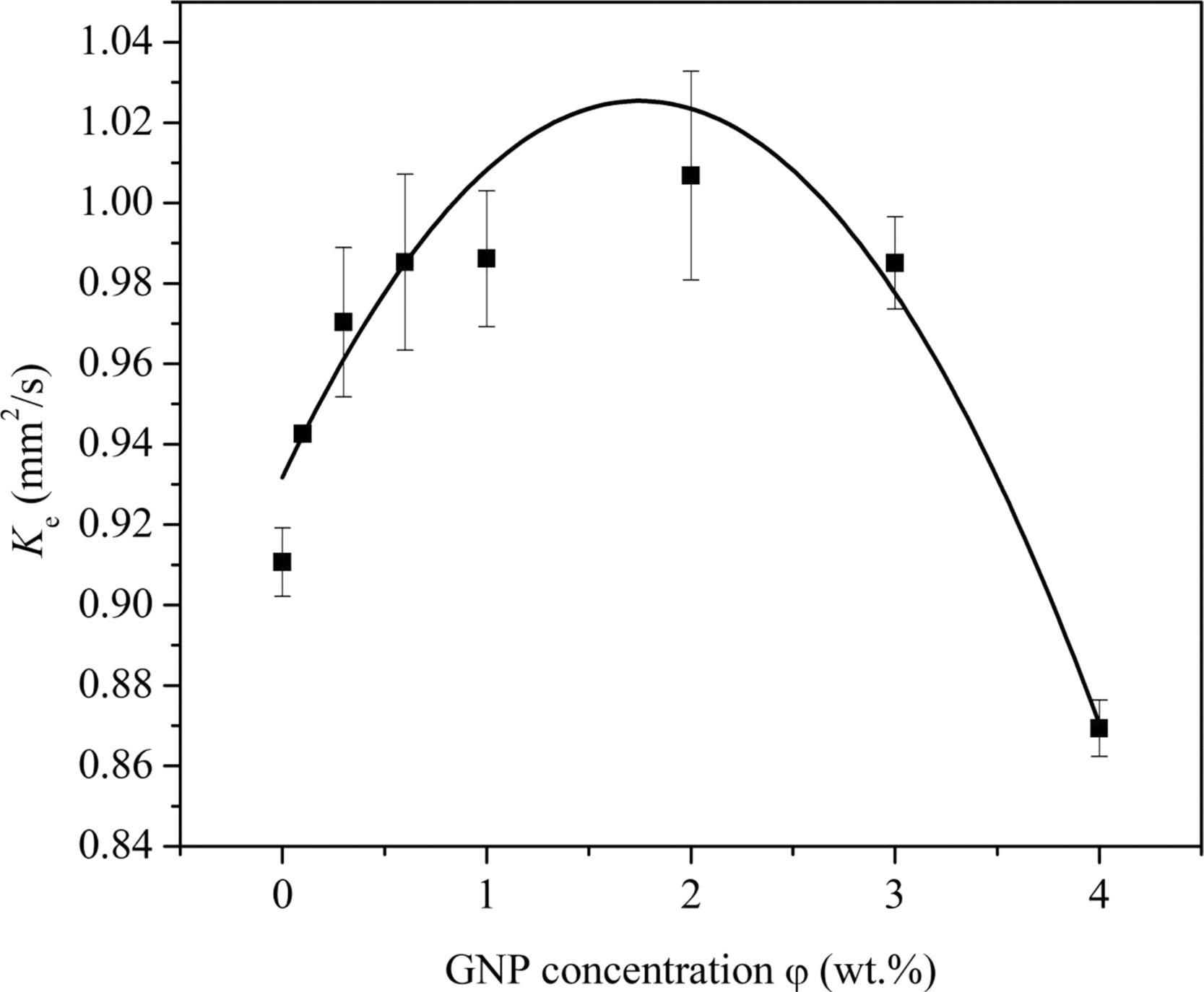
Figure 3. Evaporation rate constants of GNP/n-decane nanofluid fuels under different GNP concentrations (SP-80 of 1.0 vol %, Tair of 600 °C). Li, S., Yang, Q., et al. (2022).
The evaporation behavior was discussed in length. It may be related to several elements, including nanoplatelet aggregation, changes in physical and heat-transfer characteristics due to the nanoparticle concentration effect, surfactant concentration, and ambient temperature.
Surfactant concentration has a binomial influence on evaporation rate, while ambient temperature has a linear effect. This research would aid in developing nanofluid fuels' physical and heat-transfer properties, as well as their evaporation characteristics, for use in turbine and ramjet engines.
Continue reading: Applying Nanocoatings to Aviation: A Review.
Reference
Li, S., Yang, Q., et al. (2022). Effect of Nanoparticle Concentration on Physical and Heat-Transfer Properties and Evaporation Characteristics of Graphite/n‑Decane Nanofluid Fuels. ACS Omega. Available at: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsomega.1c05343
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.