New research has reported the conjugated dual-size effect of core-shell bimetallic nanocatalysts for the first time, where the activity of the catalysts increases with the core size in the benzyl alcohol oxidation reaction. The study was carried out by a research group headed by Professor Junling Lu, partnering with Professor Weixue Li and Professor Shiqiang Wei’s team.
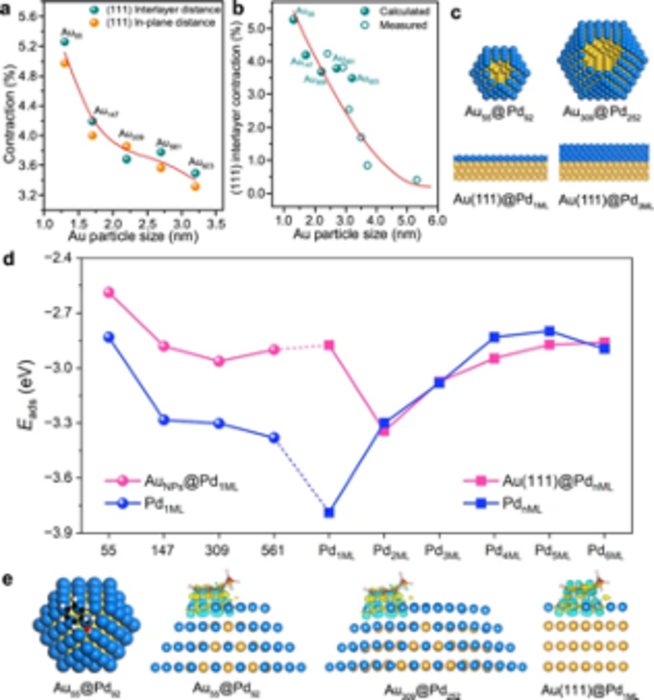 The core size and shell thickness effects on the geometric and electronic properties. Image Credit: ZHANG Xiaohui et al.
The core size and shell thickness effects on the geometric and electronic properties. Image Credit: ZHANG Xiaohui et al.
Their study has been reported in the Nature Communications journal.
Bimetallic catalysts are extensively utilized in various chemical syntheses for their bimetallic synergy differing with structures and compositions. Compared to the alloy catalysts, the strange lattice strains and ligand effects of core-shell catalysts could improve electronic and geometric properties.
The thickness of the shell considerably impacts bimetallic synergy since the ligand effects and the charge shifts between components generally take place at the core-shell interface.
As a result of the lattice mismatch between the metal core and the shell, the lattice strains in the core-shell catalyst take place. This has a notable impact on the electronic structure of the metal shell and the entire activity of catalysts.
When the core size is decreased, its lattice contracts significantly, which tends to impact its mismatch with the shell lattice, and considerably modulates the lattice strains present in the shell. This dual-size effect of core-shell particles has not yet been explored as a result of the huge difficulty in adjusting the shell thickness and core size at an atomic level.
For such hardships to be resolved, the three groups selected solvent-free selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol (BzOH) as a probe reaction and determined the dual size effect of Au@Pd catalyst with the help of multi-spectroscopy, atomic layer deposition, and density functional theory (DFT) calculations.
The theoretical calculations performed by Professor Weixue’s Li team revealed that the lattices of Pd overlayer on Au particles extend and tend to improve BzOH adsorption, while a reduced Au core size would help decrease the strains present on the Pd shell.
Additional calculations discovered that the ligand effects of Au core would significantly undermine the BzOH adsorption but could turn negligible when the Pd shell thickness went up to 2 monolayers (ML) and beyond. Hence, the highest adsorption energy could be achieved if the large-sized Au core has been covered by 2 ML thick Pd shell.
To analyze the dual size effect experimentally, Professor Junling Lu’s group initially synthesized Au/SiO2 catalysts with various Au sizes and performed Pd ALD to yield Pd shells with an altering thickness on Au particles at the atomic level.
Further, by making use of transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-Ray diffraction (XRD), the team disclosed the progress of the electronic and atomic structure of Pd and Au in the core-shell structure with the Au core size and Pd shell thickness.
The study outcomes displayed that in the oxidation of BzOH, with a fixed Au core size, the activity of catalysts was higher with Pd shell thickness rapidly and went high at 2.9 ML before it started to drop.
Also, with a fixed Pd shell thickness, the activity is enhanced with increased core size. The group obtained an utmost activity higher than the earlier studies in [email protected] catalyst.
A similar conjugated effect was discovered in the hydrogenation of para-chloronitrobenzene (p-CNB), displaying the universality of the effect. This work offered considerable guidelines for the future design of highly effective bimetallic catalysts.
Journal Reference:
Zhang, X., et al. (2023) Conjugated dual size effect of core-shell particles synergizes bimetallic catalysis. Nature Communications. doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-36147-2.
Source: https://en.ustc.edu.cn/