Oct 14 2014
The National Physical Laboratory (NPL) would like to congratulate Eric Betzig, Stefan W Hell and William E Moerner for their award of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2014. NPL scientists are building upon their pioneering work, which has resulted in 'microscopy becoming nanoscopy'.
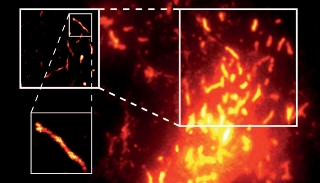 A conventional fluorescence image of a cell overlaid with super-resolution images zooming into an individual organelle (a Weibel-Palade body)
A conventional fluorescence image of a cell overlaid with super-resolution images zooming into an individual organelle (a Weibel-Palade body)
Super-resolution microscopes use the fluorescence of molecules to build up images at a higher resolution than was presumed possible for most of the 20th century. This allows scientists to see near molecular-level detail inside cells, including structures such as proteins and viruses.
Optical microscopes have a resolution limit based on the wavelength of light, around 250 nanometres (nm), which means anything smaller will appear blurred. Super-resolution techniques bypass this limit. The Nobel Prize was awarded specifically for two techniques: stimulated emission depletion (STED), which was proposed by Stefan Hell in 1994; and single-molecule microscopy, to which Betzig and Moerner contributed fundamental insights over a number of years.
In collaboration with the University of Cambridge, NPL has implemented a variant of the single-molecule microscopy technique known as STORM (stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy), which can achieve resolutions up to 10 times better than traditional optical microscopes.
It does this by using fluorescent dyes to label molecules within cells. These dyes can be switched on and off, and by doing so the centre position of each individual fluorescent molecule can be identified and plotted. The process is repeated thousands of times to build up a highly detailed, super-resolution image using all of the plotted positions from every repetition.
Alex Knight, who leads NPL's work on super resolution imaging, said: "I remember getting very excited when first seeing the research papers on super-resolution microscopy and this led us to apply for funding to develop a STORM capability at NPL. The challenge now is to keep improving the speed and resolution of these techniques, so they can be used to study ever smaller cellular structures and improve our fundamental understanding of disease. There's also a need to support the users of the techniques so that they can have confidence in the results they get."
NPL is also working with a complementary technique known as 'structured illumination microscopy' (SIM). This can produce images with a less impressive resolution than STORM, at around double that of traditional microscopes, but it works with a greater range of fluorescent dyes and is also far quicker, enabling dynamic processes to be followed in live cells.
Funding for NPL's work on super-resolution imaging has been provided by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) and the UK's National Measurement System, which is delivered through the National Measurement Office (NMO), an executive agency of the Department for Business, Innovation and Skills (BIS).
Watch the announcement of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2014
Full details of the prize winners and associated institutions:
- Eric Betzig, Janelia Research Campus, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Ashburn, USA
- Stefan W Hell, Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry and German Cancer Research Center, Germany
- William E Moerner, Stanford University, USA
Source: http://www.npl.co.uk/