Jun 4 2010
Quantum teleportation is not the same as the teleportation most of us know from science fiction, where an object (or person) in one place is "beamed up" to another place where a perfect copy is replicated. In quantum teleportation two photons or ions (for example) are entangled in such a way that when the quantum state of one is changed the state of the other also changes, as if the two were still connected. This enables quantum information to be teleported if one of the photons/ions is sent some distance away.
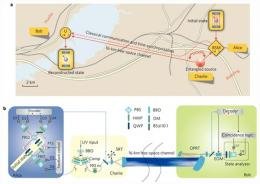 A birds-eye view of the 16-km free-space quantum teleportation experiment. Charlie sends photon 1 to Alice for BSM. Classical information, including the results of the BSM and the signal for time synchronization, is sent through the free-space channel with photon 2, to Bob, before decoding and triggering of the corresponding unitary transformation. b, Sketch of the experimental system. See the original paper for more details. Image: Nature Photonics.
A birds-eye view of the 16-km free-space quantum teleportation experiment. Charlie sends photon 1 to Alice for BSM. Classical information, including the results of the BSM and the signal for time synchronization, is sent through the free-space channel with photon 2, to Bob, before decoding and triggering of the corresponding unitary transformation. b, Sketch of the experimental system. See the original paper for more details. Image: Nature Photonics.
In previous experiments the photons were confined to fiber channels a few hundred meters long to ensure their state remained unchanged, but in the new experiments pairs of photons were entangled and then the higher-energy photon of the pair was sent through a free space channel 16 km long. The researchers, from the University of Science and Technology of China and Tsinghua University in Beijing, found that even at this distance the photon at the receiving end still responded to changes in state of the photon remaining behind. The average fidelity of the teleportation achieved was 89 percent.
The distance of 16 km is greater than the effective aerosphere thickness of 5-10 km, so the group's success could pave the way for experiments between a ground station and a satellite, or two ground stations with a satellite acting as a relay. This means quantum communication applications could be possible on a global scale in the near future.
The public free space channel was at ground level and spanned the 16 km distance between Badaling in Beijing (the teleportation site) and the receiver site at Huailai in Hebei province. Entangled photon pairs were generated at the teleportation site using a semiconductor, a blue laser beam, and a crystal of beta-barium borate (BBO). The pairs of photons were entangled in the spatial modes of photon 1 and polarization modes of photon 2. The research team designed two types of telescopes to serve as optical transmitting and receiving antennas.
Original Paper:http://www.nature.com/nphoton/journal/v4/n6/full/nphoton.2010.87.html
Source: Chinese Academy of Sciences