A research team comprising Elizabeth Strychalski, Samuel Stavis and colleagues from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has developed an innovative nanofluidic technology to control and measure Nanomaterials and DNA molecules.
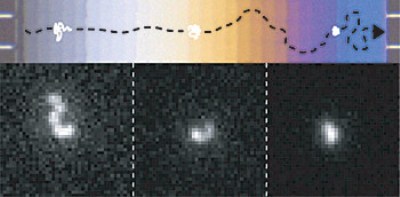 Schematic showing the motion of a DNA molecule descending a nanofluidic staircase by entropophoresis (top). The illustration is overlaid on a micrograph of the actual staircase. Lightwave interference gives each step a different color. Corresponding fluorescence micrographs (bottom) show how the DNA molecule contracts as the depth increases from about 4 nanometers (about 20 times bigger than a water molecule) at the left to about 342 nanometers at the deepest step on the right. The images of the DNA molecule are blurred and pixilated, making it appear larger than it is. These imaging errors are estimated and corrected in the final analysis of the size of the molecule. (Credit: Strychalski, Stavis/NIST)
Schematic showing the motion of a DNA molecule descending a nanofluidic staircase by entropophoresis (top). The illustration is overlaid on a micrograph of the actual staircase. Lightwave interference gives each step a different color. Corresponding fluorescence micrographs (bottom) show how the DNA molecule contracts as the depth increases from about 4 nanometers (about 20 times bigger than a water molecule) at the left to about 342 nanometers at the deepest step on the right. The images of the DNA molecule are blurred and pixilated, making it appear larger than it is. These imaging errors are estimated and corrected in the final analysis of the size of the molecule. (Credit: Strychalski, Stavis/NIST)
The research team has named the technology as nanoslinky as it resembles Slinky, a coiled metal spring. The novel technology featuring a nanofluidic channel with a staircase shape offers more benefits over conventional nanofluidic methods used for controlling and measuring DNA molecules.
Stavis explained that the staircase structure controls a DNA molecule’s behavior. After the DNA molecule was positioned on the top step of the staircase with the help of an electric field, it started moving without any external forces. The staircase structure is a passive nanofluidic technology, which automates complicated measurements and manipulations of DNA molecules.
This NIST nanofluidic technology advancement merges well with a NIST measurement science innovation developed for detecting a DNA molecule’s size in a nanofluidic ‘slit-like confinement’ created by the narrow space between the channel’s ceiling and steps’ floor. Strychalski informed that the folded and coiled DNA strand contractsgradually when it descends the steps in the nanoslinky system. The novel technology provides more accurate measurements than earlier studies as there are many steps in the system.
To more accurately measure the DNA molecules when they move down, the NIST team utilized models to approximate the consequences of pixilation and diffraction. The researchers obtained the most quantitative final measurements of the size of DNA molecules by applying these numerical models to the pictures of the DNA molecules trapped by the staircase. These measurements also demonstrated that more research is required to comprehend this complex system.
According to the researchers, the staircase technology is a basic prototype of engineered nanofluidic structures that have complicated 3D surfaces. The fine-tuned technology may one day be volume manufactured for manipulating and measuring not only DNA molecules but also nanomaterials and biopolymers for nanomanufacturing and healthcare.