Nov 20 2008
In a superconductor, when the temperature drops below a critical value (Tc), its electrical resistance vanishes. Scientists interested in this phenomenon are striving to understand its origin so they can determine how to obtain the highest values of Tc.
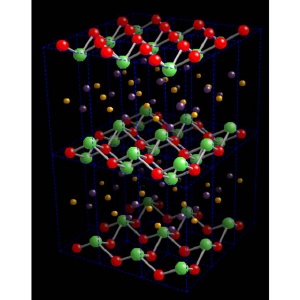 Ball and stick structure of LaFeAsO. The different colors represent the different atoms (Yellow: Fe, Green: La, Red: O, Purple: As). LaFeAsO1–xFx is obtained by substituting some of the O atoms with F).
Ball and stick structure of LaFeAsO. The different colors represent the different atoms (Yellow: Fe, Green: La, Red: O, Purple: As). LaFeAsO1–xFx is obtained by substituting some of the O atoms with F).
It is commonly accepted that the absence of resistivity is connected to the formation of electron pairs. In 'traditional' superconductors, where Tc is lower than 30 K (-243 °C), the pairing is attributed to interaction of electrons within the lattice of the material. But for the past 20 years, scientists have been puzzling over why this does not apply to high Tc superconductors of the cuprate family, with Tc values up to 150 K (-123 °C).
A few months ago, another family of superconductors called iron pnictides—based on iron and arsenic—were discovered, also with relatively high Tc (up to 55 K (-218 °C)). To determine whether the pairing mechanism for iron pnictides is similar to that of the cuprates, researchers at the RIKEN Advanced Science Institute, Wako, and colleagues in Japan have built a theoretical model that could prove essential to our understanding of how superconductivity arises in these materials*.
The researchers focussed on the first member of the new superconducting family, LaFeAsO1–xFx. They realized that before examining the pairing mechanism it was necessary to build an electronic model that describes the low-energy physics of this material.
As team-member Ryotaro Arita explains “the electronic structure of LaFeAsO1–xFx is much more complicated than that of the cuprates.” In cuprates, it is widely believed that only one of the five outer orbitals of copper (Cu) is important. In LaFeAsO1–xFx, however, the team has found that the effective model involves all five outer orbitals of iron (Fe).
In the second part of the work, Arita and co-workers searched for the most favorable electron pairing 'symmetry' and found that the so-called 'extended' s-wave pairing—involving electrons on 'neighboring' sites—is likely to be dominant.
The results were obtained with a theoretical method known as random phase approximation (RPA), which is a common but relatively simple technique used to describe many-body interactions. “Of course, we are not satisfied with RPA, and indeed we are now going beyond that,” says Arita. Meanwhile, the model is readily available to study the mechanism/properties of superconductivity in iron pnictides. “I believe that the information on the effective model provided in our paper is very important for the field.”
- Kuroki, K., Onari, S., Arita, R., Usui, H., Tanaka, Y., Kontani, H. & Aoki, H. Unconventional pairing originating from the disconnected Fermi surfaces of superconducting LaFeAsO1–xFx. Physical Review Letters 101, 087004 (2008).