Improving the permeability and separation selectivity for H+/organics of a poly(amide-sulfonamide) acid-resistant nanofiltration membrane via a catalytic template assisted interfacial polymerization strategy. Image Credit: Yang Cao
The study was released in the AIChE Journal on January 14th, 2023.
Commercially available NF membranes frequently exhibit poor performance and stability in the treatment of acidic wastewater because they are acid sensitive.
Current acid-resistant NF membranes have very low permeability and low separation selectivity for H+/organics due to the low reactivity of acid-stable monomers.
To increase separation selectivity for H+/organics, the researchers aimed to increase membrane permeability and enhance separation layer homogeneity.
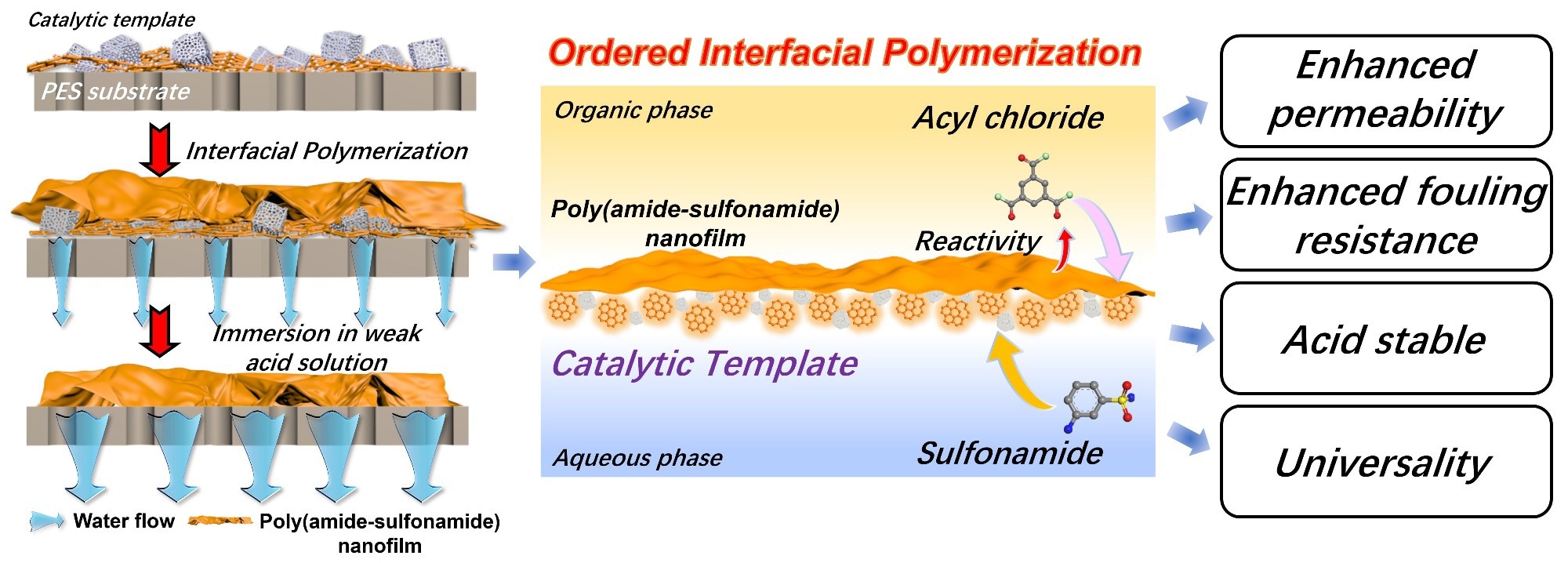
They synthesized aminopyridine-doped graphene quantum dot acylation catalysts, which were grown in situ as a sacrificial template on a porous substrate and co-loaded with ZIF-8 nanoparticles.
Then, to create the acid-resistant poly(amide-sulfonamide) network, the 3-aminobenzenesulfonamide with a strong conjugation effect was chosen as the aqueous monomer to react with trimesoyl chloride.
The resulting ultra-thin membrane displayed excellent water permeance (20.4 Lm–2h–1bar–1) and Na2SO4 rejection of 90.5%, benefiting from increased monomer reactivity and optimized phase integrity.
The membrane demonstrated pigment/H+ selectivity that was superior to the commercial GE Duracid membrane at 8 wt% H2SO4 condition, even for wastewater that was actually acidic from cane molasses. This was possible owing to the membrane’s acid-stable polysulfonamide backbone, low layer thickness, and narrow pore size distribution.
Combining a conventional acylation catalyst with a novel nanoparticle carrier, we developed a new scalable strategy for synthesis of special separation membranes. Our work also offers a new horizon for utilizing more monomers with special structure for synthesis of functional polymers via interfacial polymerization method.
Jianquan Luo, Study Corresponding Author and Professor, Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Journal Reference
Cao, Y., et al. (2022) Catalytic Template Assisted Interfacial Polymerization for High-performance Acid-resistant Membrane Preparation s. AIChE Journal. doi:10.1002/aic.18038.