Jan 22 2009
Solitary waves, known as solitons, can be striking. The first observation of a soliton was documented in 1834: a large moving heap of water formed by a boat on a canal in Scotland. Since then, solitons have been found in many areas of science including nonlinear optics, condensed matter physics, astrophysics (for example Jupiter's red spots), and biology (during energy transfer in DNA).
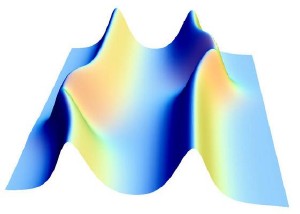 A two-dimensional magnetic field distribution of hill-shaped vortex lines in a superconducting Josephson junction, with smaller 'shape excitations' on top. These 'shape waves' can be considered as solitons propagating along other solitons. They can be used to measure a time dilation effect analogous to that in special relativity.
A two-dimensional magnetic field distribution of hill-shaped vortex lines in a superconducting Josephson junction, with smaller 'shape excitations' on top. These 'shape waves' can be considered as solitons propagating along other solitons. They can be used to measure a time dilation effect analogous to that in special relativity.
Solitons can also be found in a so-called Josephson junction, where a thin insulating layer is sandwiched between two superconductors. A team, including RIKEN scientists at the Advanced Science Institute in Wako, has discovered a new type of soliton excitation in a Josephson junction that could be used to measure time dilation effects similar to those in Einstein's special relativity1.
In a Josephson junction, the role of a soliton is played by a 'Josephson vortex'-a lump of magnetic field that can be accelerated inside the material2. When a Josephson vortex approaches the speed of light for the material, it should start to experience relativistic effects. One of these effects, the Lorentz (length) contraction of solitons, has been observed in experiments. However the measurement of another relativistic effect, time dilation, has been a challenge.
"It has been difficult to observe time dilation for a moving Josephson vortex because we need something internal acting as a clock to measure time in its frame of reference," explains team member Franco Nori from RIKEN and the University of Michigan, USA. "We can't find such a clock in conventional Josephson junctions, but we found one that can exist in vortices in long, wide Josephson junctions."
The 'clock' discovered by Nori and co-workers is a nonlinear wave that propagates along Josephson vortices, and therefore belongs to the vortex frame of reference. The excitations are associated with distortions in the Josephson vortices, and are similar to shear waves in solids. They can have almost any shape and retain it for a long time while the wave is propagating.
"The new excitation that we discovered can act as the 'minute hand' of a clock, keeping track of time in the frame of reference of a moving soliton," says team member Dmitry Gulevich from Loughborough University, UK, and RIKEN.
Feo Kusmartsev and Sergey Savel'ev, also from Loughborough University, add: "This effect could be used to transmit information, and as waveguides for Terahertz radiation." The research team plans to put the predicted effect into practice in the near future.
- Gulevich, D.R., Kusmartsev, F.V., Savel'ev, S., Yampol'skii, V.A. & Nori, F. Shape waves in 2D Josephson junctions: Exact solutions and time dilation. Physical Review Letters 101, 127002 (2008).
- Gulevich, D.R., Savel'ev, S., Yampol'skii, V.A. Kusmartsev, F.V. and Nori, F. Josephson vortices as flexible waveguides for terahertz waves. Journal of Applied Physics 104, 064507 (2008).