Modern technology has revolutionized many industries.
Every year, new alterations and materials are produced; however, these materials are generated by advanced industries, and leftovers are discharged into the air, water, soil, and nature, causing pollution.
It is one of the most serious issues that any country faces. The principal pollutants that affect the environment include fine particles, toxic substances, insecticides, fertilizers, oil spills, poisonous gases, industrial discharges, wastewater, and chemical molecules.
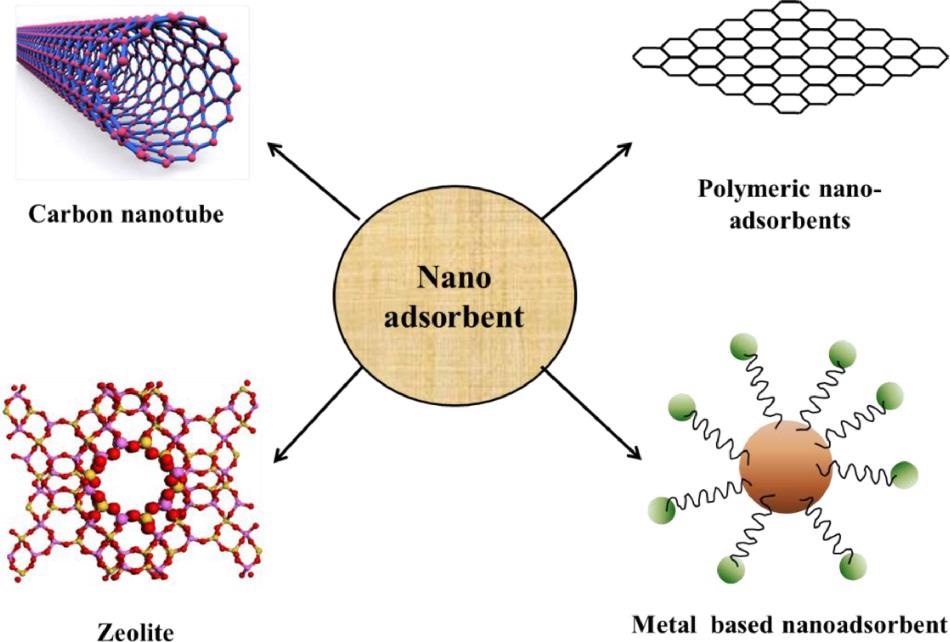
Classification of nanoadsorbent © Ningthoujam, R. et. al. (2022)
What is a Nano-Adsorbent?
Owing to their physicochemical features, such as extremely high surface area, many adsorption locations, different temperatures alteration, low intraparticle distances, variable pore diameter, and surface composition, these nanomaterials are particularly effective adsorbents in wastewater treatment.
They include carbon nanotubes, polymeric nano-adsorbents, zeolites, and metal adsorbents.
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are constructed of carbon nano cylindrical with single or multi-walled nanotubes. CNTs have a greater surface area and many adsorption sites.
The contact between CNTs and transition metals is performed via electrostatic forces which aid in the removal of oil particles from polluted water.
Polymeric nano-adsorbent with a high surface-to-volume ratio, flexible surface chemistry, optimum tensile stiffness, and porous structure makes it a more powerful technology than the standard method and more practicable in some conditions.
Zeolites are microporous materials with electrostatic holes formed of alumina and silica minerals that have a large surface area that is occupied by cations and water molecules.
Microbial growth has been observed to be inhibited by zeolites containing silver coupling. These are aluminosilicate compounds with a high density of surface electrostatic holes.
Finally, metal-based nano-adsorbents have been shown to be more effective than activated carbon at removing contaminants and radioactive elements. Because of their large surface area, they have a short intraparticle length and may be readily compacted without affecting the surface area.
Role of Nanocatalysts in Decrement of Pollutants
Nanocatalysts are generally composed of metallic nanoparticles and semiconductors, and they have a great potential for action against germs, pathogens, radioisotopes, and organic pollutants.
Nanocatalysts are often proposed as an alternate way to assist in addressing global water contamination. Surface coatings in membrane separation, screens, adsorption materials, and polymeric surfaces of nanomaterials, as well as reagents, have all been made possible by nanoparticles and nanotechnology.
The large surface area of nanocatalysts enables for greater adsorption process, attracting pollutants to bind to the particles by chemical adsorption or physical adsorption, depending on the functional alteration of the nano adsorbent.
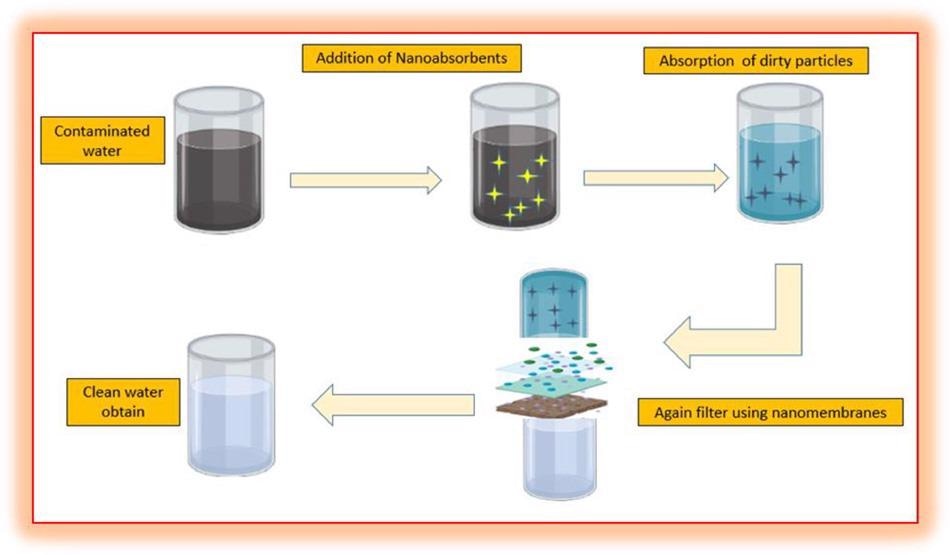
Process involve in the removal of metal ions. © Ningthoujam, R. et. al. (2022)
Effectiveness of Nanomembranes
The advancement of technology is accelerating, and nanomembranes are one of its products. Nanomembranes are installed to control some of their problems during the clean-up procedure.
Nanomembranes are synthesized barriers with a thickness of less than 100 nm, and are used for the removal of excess salts from saline water to obtain drinkable water. Additionally, they are used for commercial treatment of sewage and air filtration due to their significant benefits.
In conclusion, several types of nanoparticles are effectively used in a multitude of climate pollution remediation. However, further research into low-cost nano products would be extremely beneficial in this area.
Reference
Ningthoujam, R. et. al. (2022). Nanocatalyst in remediating environmental pollutants. Chemical Physics Impact. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chphi.2022.100064
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.