Through the development of new technology, a research group headed by Associate Professor Shota Kuwahara of Toho University and Associate Professor Masato Kuwahara of Nagoya University can create three-dimensional structures of gold nanoparticles contained within silica nanocapsules.
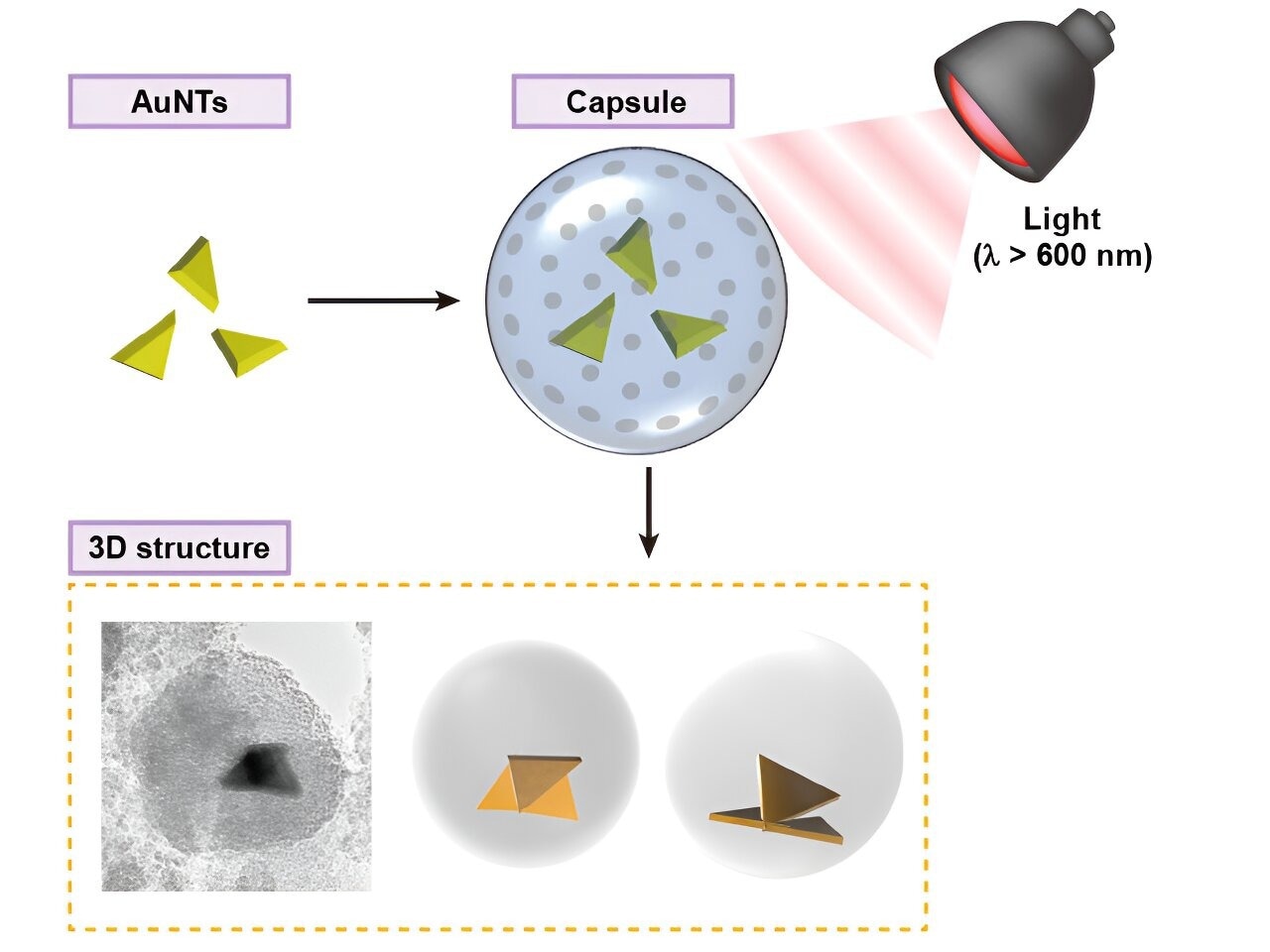 Schematic image of three-dimensional building of anisotropic gold nanoparticles under confinement in submicron capsule. Image Credit: Dr. Shota Kuwahara
Schematic image of three-dimensional building of anisotropic gold nanoparticles under confinement in submicron capsule. Image Credit: Dr. Shota Kuwahara
It is anticipated that the built three-dimensional nanostructures would display novel physical characteristics. Additionally, their distinct optical qualities may facilitate the advancement of technologies like highly sensitive multi-color sensors. The research findings were released in Nanoscale Advances.
Strong electric fields can fuse metallic nanoparticles when they are exposed to light that corresponds to localized surface plasmon resonance. This process is reliant on the form of the nanoparticles and can be induced in a position-specific way. The objective of this work was to expand the unique optical features of gold nanoparticles by creating higher-order structures through the use of this approach.
Due to the limited contact orientation and low contact probability between gold nanoparticles, it has proven challenging to create higher-order structures out of them thus far.
In this study, the researchers created a place where gold nanoparticles could contact each other from all directions by enclosing numerous nanoparticles in a mesoporous silica shell that was submicron in size. This enhanced the contact probability between the nanoparticles and is the first report of successful three-dimensional gold nanostructure manufacturing.
The three-dimensional gold nanostructures generated by this process were observed with a scanning transmission electron microscope (STEM), and calculations for electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS) mapping were carried out based on these images. The findings showed that the energy of the incident electromagnetic field generates several plasmon modes and that the plasmon mode of the three-dimensional structure affects the location of hot spots.
Journal Reference:
Yamada, R., et. al. (2023) Three-dimensional building of anisotropic gold nanoparticles under confinement in submicron capsules. Nanoscale Advances. doi:10.1039/D3NA00683B