Oct 22 2009
HRL scientists announced today they have fabricated and demonstrated graphene-on-silicon field effect transistors (FETs) at full wafer scale-a revolutionary advancement in electronics that will enable unprecedented capabilities in high-bandwidth communications, imaging and radar systems. The work is part of the Carbon Electronics for RF Applications, or CERA program, sponsored by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) and under the management of the Space and Naval Warfare Systems Center. HRL has been collaborating with a group of universities, commercial companies and the Naval Research Laboratory on the program.
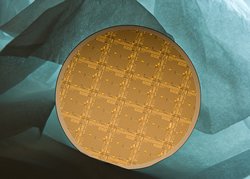
The goal of CERA is to exploit the unique physical characteristics of graphene to create electronic components that will provide game-changing enhancements to imaging, radar and communications applications, which have been hindered by component cost, limited resolution and high power dissipation. Graphene—a single layer of carbon atoms densely packed in a tight, honeycomb crystalline lattice configuration—has enormous potential because of its extremely high current-carrying capacity, excellent thermal conductivity and low-voltage operation.
The challenge was to integrate graphene onto a silicon platform to reap the benefits the material provides. "In collaboration with the Electro-Optics-Center at Pennsylvania State University, which is a member of the CERA research team, HRL has demonstrated the feasibility of graphene-on-silicon technology," said Dr. Jeong Sun-Moon, a Senior Scientist in HRL's Microelectronics Laboratory and Principal Investigator for the CERA program.
HRL began work on CERA in July 2008, reaching an initial milestone in December 2008 by successfully integrating and demonstrating the world’s first graphene FETs in the RF frequency range. Researchers then took the technology to the next level by demonstrating epitaxial graphene FETs on a two-inch wafer scale that consisted of graphene on silicon carbide.
The latest breakthrough of demonstrating silicon-on-graphene brings the team one step closer to meeting the goals of the CERA program. "Silicon-compatible graphene technology would open the potential to a much more efficient, higher power, lower cost graphene technology, as well as the possibility of co-integrating graphene FETs and silicon-CMOS FETs," Moon said. "Although many technological challenges remain, our results represent a significant first step toward achieving graphene-on-silicon technology."