May 2 2019
Chinese scientists from the Institute of Intelligent Machines, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science achieved highly sensitive detection of Pb(II) that is extremely difficult to precisely detect for its low concentration in drinking water.
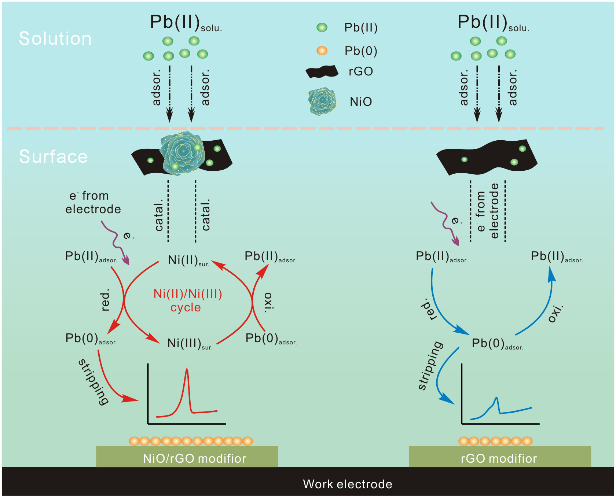 Schematic of electroanalysis for Pb(II) based on adsorption and catalytic mediation of Ni(II)/Ni(III) cycle of NiO/rGO nanocomposite. (Image credit: YANG Meng)
Schematic of electroanalysis for Pb(II) based on adsorption and catalytic mediation of Ni(II)/Ni(III) cycle of NiO/rGO nanocomposite. (Image credit: YANG Meng)
The group developed porous flower-like NiO/rGO nanocomposite to get over issues in the detection and were able to realize high-performance sensitive sensing of Pb(II) with square-wave anodic stripping voltammetry (SWASV).
In the research, they discovered the outstanding performance of NiO/rGO nanocomposite customized electrode for Pb(II) analysis by integrating the good catalysis of NiO with high conductivity and adsorption of rGO, and also the improved redox activity by Ni(II)/Ni(III) cycling on the surface of NiO/rGO nanocomposite.
They further tested their approach by conducting it in a real water environment. As reported by the test conducted in wastewater obtained from a sewage disposal plant in the local community, the team yielded a good test result that was in agreement with it in the lab.
This research was supported by the postdoctoral innovation talents supporting the project, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the technology major project of Anhui Province, and the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province, the postdoctoral researcher funding project of Anhui Province.