Feb 26 2014
Cleaning up oil spills and metal contaminates in a low-impact, sustainable and inexpensive manner remains a challenge for companies and governments globally.
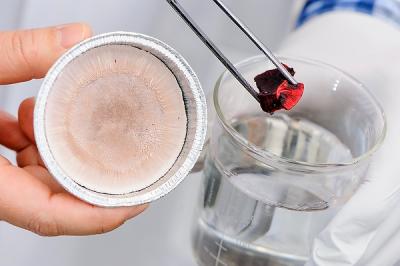 As seen on Feb. 11, 2014, Shaoqin 'Sarah' Gong, a researcher at the Wisconsin Institute for Discovery and associate professor of biomedical engineering at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, graduate student Qifeng Zheng, and Zhiyong Cai, a project leader at the US Department of Agriculture Forest Products Laboratory in Madison, have recently created and patented a new aerogel technology that may offer a cheaper and greener method to absorb oil and heavy metals from water and other surfaces. Pictured here, Zheng uses tweezers to hold a sample of the aerogel that has been used to absorb red-dyed diesel fuel (right), while Gong holds a sample of unused aerogel (left). Credit: Bryce Richter/University of Wisconsin Madison
As seen on Feb. 11, 2014, Shaoqin 'Sarah' Gong, a researcher at the Wisconsin Institute for Discovery and associate professor of biomedical engineering at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, graduate student Qifeng Zheng, and Zhiyong Cai, a project leader at the US Department of Agriculture Forest Products Laboratory in Madison, have recently created and patented a new aerogel technology that may offer a cheaper and greener method to absorb oil and heavy metals from water and other surfaces. Pictured here, Zheng uses tweezers to hold a sample of the aerogel that has been used to absorb red-dyed diesel fuel (right), while Gong holds a sample of unused aerogel (left). Credit: Bryce Richter/University of Wisconsin Madison
But a group of researchers at the University of Wisconsin–Madison is examining alternative materials that can be modified to absorb oil and chemicals without absorbing water. If further developed, the technology may offer a cheaper and "greener" method to absorb oil and heavy metals from water and other surfaces.
Shaoqin "Sarah" Gong, a researcher at the Wisconsin Institute for Discovery (WID) and associate professor of biomedical engineering, graduate student Qifeng Zheng, and Zhiyong Cai, a project leader at the USDA Forest Products Laboratory in Madison, have recently created and patented the new aerogel technology.
Aerogels, which are highly porous materials and the lightest solids in existence, are already used in a variety of applications, ranging from insulation and aerospace materials to thickening agents in paints. The aerogel prepared in Gong's lab is made of cellulose nanofibrils (sustainable wood-based materials) and an environmentally friendly polymer. Furthermore, these cellulose-based aerogels are made using an environmentally friendly freeze-drying process without the use of organic solvents.
It's the combination of this "greener" material and its high performance that got Gong's attention.
"For this material, one unique property is that it has superior absorbing ability for organic solvents — up to nearly 100 times its own weight," she says. "It also has strong absorbing ability for metal ions."
Treating the cellulose-based aerogel with specific types of silane after it is made through the freeze-drying process is a key step that gives the aerogel its water-repelling and oil-absorbing properties.
"So if you had an oil spill, for example, the idea is you could throw this aerogel sheet in the water and it would start to absorb the oil very quickly and efficiently," she says. "Once it's fully saturated, you can take it out and squeeze out all the oil. Although its absorbing capacity reduces after each use, it can be reused for a couple of cycles."
In addition, this cellulose-based aerogel exhibits excellent flexibility as demonstrated by compression mechanical testing.
Though much work needs to be done before the aerogel can be mass-produced, Gong says she's eager to share the technology's potential benefits beyond the scientific community.
"We are living in a time where pollution is a serious problem — especially for human health and for animals in the ocean," she says. "We are passionate to develop technology to make a positive societal impact."