Nanodiamonds (NDs) are utilized in various applications owing to their exceptional bulk properties. They enhance lubricants and polishing materials, act as fillers in electroplated films, and improve polymer coatings by boosting mechanical properties and thermal resistance. Additionally, they contribute to the development of materials and formulations resistant to UV and radiation.
However, applications in drug delivery, composites, and biomolecule immobilization depend on the surface characteristics.
NDs are incredibly flexible materials with many uses due to their unique bulk and surface properties. Some of the key applications of NDs encompass their use in drug delivery, polymer strengthening, facilitating high-density nucleation and growth of CVD diamond films, serving as additives in oils, lubricants, and fuels, supporting catalysts, and as materials for antibacterial and antifungal coatings.
Due to their exceptional mechanical and chemical characteristics, along with their small size and roughly spherical form, NDs are perfect for the applications indicated above.
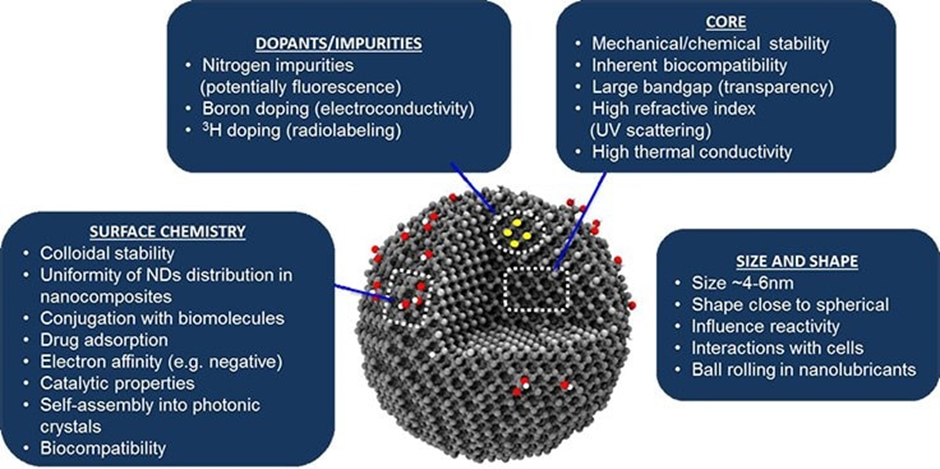
Figure 1. Critical features of DND primary particles and resultant properties and applications. Image Credit: Merck
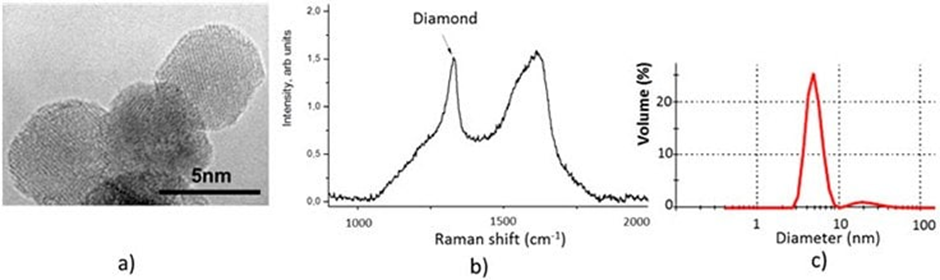
Figure 2. Characteristics of nanodiamond particles: (a) high resolution transmission electron microscopy image. (b) Raman shift demonstrating pronounced nanodiamond peak at 1326 cm-1 and (c) volumetric particle size distribution from dynamic light scattering analysis demonstrating high monodispersity of 4-6 nm ND particles dispersed in DI water. Image Credit: Merck
Other Notes
Do not freeze the components.
Materials
Source: Merck
| . |
. |
 |
Monodispersed nanodiamond particles dispersion, 5 nm avg. part. size (DLS), carboxylated |
 |
Monodispersed nanodiamond particles 5 nm avg. part. size (DLS), 10 mg/mL in DMSO, hydroxylated |
 |
Monodispersed nanodiamond particles 5 nm avg. part. size (DLS), 10 mg/mL in H2O, carboxylated |
 |
Monodispersed nanodiamond particles 5 nm avg. part. size (DLS), 10 mg/mL in DMSO |
 |
Nanodiamonds 65 nm, dodecane functionalized, powder |
 |
Nanodiamonds 65 nm octadecane functionalized, powder |